Mastering Secure Remote Access: 10 Best Practices for Enhanced Cybersecurity
While remote employment had been practiced before 2020, the Covid-19 outbreak served as the impetus for it to become widely accepted. This increased the necessity for users to access corporate networks on an as-needed basis, forcing these networks to provide simultaneous access from many locations. As many employees were now utilizing personal devices, the great majority of connections were now coming from their home networks. This increased the hazards that both business and personal networks faced and frequently rendered older security mechanisms obsolete.
This started off as a technical issue. Yet, many firms are now free to recruit people based on qualifications rather than geography since they have learned about the cultural and economic advantages of remote labor. On the other hand, firms that are unable to keep up with the rising standards for data and network cleanliness frequently become targets of emerging attack groups. However, security flaws continue to be at an all-time high, which has pushed safe remote access to the top of the priority lists for IT and security departments throughout the world. A new security standard is enabling remote system access for every user, from any network they dial in from, on any device they want, across all industries.
In this article, we will cover the following topics related to secure remote access:
- What is secure remote access?
- How does secure remote access work?
- What are the benefits of secure remote access?
- What are the risks associated with remote work access security?
- 10 Best Practices for Remote Work Access Security
- What is the Relationship Between ZTNA and Secure Remote Access?
- Which is Better for Secure Remote Access? ZTNA or VPN?
- What is the Relationship Between SD-WAN and Secure Remote Access?
- What is the Relationship Between SASE and Secure Remote Access?
- What is the Relationship Between Cloud Security and Secure Remote Access?
- What are the Best Secure Remote Access Tools?
What is Secure Remote Access?
IT specialists frequently employ secure remote access while assisting remote colleagues with technical issues. It's useful for managers who want to monitor what their employees are doing on business devices as well as for employees who need to log in to a secure device that is linked to their company server in the office while working from a personal device at home.
It's crucial to have security measures in place to stop any unwanted access to your programs and data if you're giving your team members access to corporate devices or systems. Secure remote access systems use a variety of techniques, tools, and software to guard against unauthorized access to computers and networks.
How Does Secure Remote Access Work?
Theoretically, a user connects to any device via either local networks or the Internet. A virtual private network (VPN) that offers a secure connection between two devices is used for remote access via the Internet. In essence, the VPN works as a tunnel to maintain the confidentiality and continuity of traffic. By serving as a gateway at the network's edge, the VPN server routes traffic to the appropriate hosts.
A router running VPN software wraps and encrypts the traffic before it is sent by a distant user. Data packets are then delivered across the Internet to a receiving destination using a flexible set of routes based on accessible network pathways. A VPN gateway, or endpoint, decrypts the communication before reassembling the packets into their original format since the traffic is encrypted. The VPN gateway then executes the reverse operation, sending an encrypted answer back to the original VPN client via the Internet.
A local network, or physical network, instead uses a single communication channel, such as a private data channel, to establish a hardwired connection between the endpoints.
What are the Benefits of Secure Remote Access?
A secure remote access method has the following advantages:
- Safe access to any device, anywhere: The same level of extremely secure access is available to users as it was previously at work. Depending on their roles and responsibilities, access controls might provide each user with access to particular programs and data. This is the most essential benefit of a secure remote access approach since many employees will continue to work from home after the COVID problem has passed.
- Strong endpoint security: If the endpoints are not secured, secure remote access is useless. Protection for computers, tablets, and smartphones is crucial as users increasingly rely on various devices to complete their tasks. Employee-owned devices should have access to the same endpoint security features as those offered by the company.
- Safe access to the Internet: Several web-based and internet-focused apps are utilized by organizations as part of their IT infrastructure. Users need safety not just while they are linked to the company's on-premises resources, but anytime they are connected to the internet. Users must be protected from web-based malware threats like phishing scams and ransomware in order to use secure remote access.
- Increases knowledge of security concerns: Many new security concerns are brought on by a workforce that is becoming more mobile, and for many of them, education is the best remedy. It is possible for IT and security companies to continuously emphasize the significance of good cybersecurity hygiene by maintaining and enforcing security rules and best practices.
What are the Risks Associated with Remote Work Access Security?
Employees inadvertently engage in poor cybersecurity practices, providing threat actors access to your network and the confidential data of your business. Employees are uncertain about how to continue working safely when business activities abruptly or temporarily shift to remote work.
The largest security danger to your network might come from remote workers, who put the data of your business at risk. Working from home has the potential to lead to identity theft, data breaches, and a range of other undesirable outcomes.
Let's examine the following security threats that businesses that use remote workers must deal with:
- Email fraud: Phishing tactics provide the biggest security hazard to remote workers. Phishing schemes involve a person or organization pretending to be a reliable source, typically over email, in order to trick a victim into providing private login credentials or privileged information. This information can then be used to access accounts, steal more sensitive data, commit identity fraud, and commit other crimes. Because phishing emails are now so sophisticated, it is getting harder for employees to recognize them, especially when they get past email filters and end up in their primary inbox.
- Weakened security measures: Beyond lax firewall regulations and email policies, security measures are being weakened significantly. Remote workers will not be covered by the various levels of cybersecurity already in place. When employees take their work gadgets home, they substitute the workplace network with their private Wi-Fi, which renders them defenseless. No cybersecurity teams are keeping an eye on what employees' home networks are doing. By definition, remote work entails some system access, network activity, and data movement beyond the typical boundaries of the corporate IT environment. Organizations often find it difficult to extend monitoring to all endpoints and across all networks, which are increasingly making remote work situations possible.
- Cyberattacks on the infrastructure for remote work: In addition to undermining current restrictions, launching new infrastructure will result in additional dangers. Server-side and brute-force attacks should be monitored by security personnel. Protection from DDoS will become crucial. This will be the first time for many firms that a DDoS assault might completely kill their business by stopping remote workers from accessing services online. Both of these assault types are anticipated to rise rapidly, according to researchers.
- Access to sensitive information through unprotected Wi-Fi networks: Your staff members can utilize unprotected public Wi-Fi to access their company accounts or connect to their personal wireless network. This makes it easy for hostile individuals nearby to observe their connection and get sensitive data. For instance, attackers may intercept and steal data provided in plain text form that is not encrypted. Because of this, you should forbid your staff from connecting to any unidentified Wi-Fi networks unless they are doing so using a VPN connection.
- Additional attack surfaces: Businesses simply have more endpoints, networking, and software to secure as a result of more employees working remotely, which adds considerably to the workload of already overworked IT staff.
- Using personal devices at work: When working from home, many employees transmit data between personal computers and the workplace, which is a concerning behavior. Moreover, a policy known as "Bring Your Own Device" (BYOD) has grown in popularity in recent years and permits employees to use their own devices at work. When permitting your workers to use their personal devices for work-related tasks, you must be completely aware of the risks involved. For instance, someone may abruptly leave the organization and keep the private information that was kept on their device while they were working there, and you wouldn't have the chance to delete it. They could not be updating their software, which exposes security gaps in your environment. We keep emphasizing how crucial it is to deploy software updates promptly, and with good cause. Because it would be challenging for you to oversee what happens on your workers' endpoints, we advise against allowing them to use their personal devices at work.
- The problem of public spaces: Although cybersecurity is our main priority, we still need to maintain physical security in order to protect the critical data belonging to your firm. For instance, some employees could work while talking loudly on the phone, display their laptop screen for everyone to see in a cafe, or even leave their equipment unattended. Even the most fundamental security precautions should be taught to employees by businesses, even if they appear obvious at first. A polite reminder to them to keep information about your company private will always be beneficial.
- Weak passwords: Even if a business uses firewalls, virtual private networks, and other cybersecurity solutions to defend its remote network, human error still happens when employees try to protect their accounts with weak passwords. Strengthening passwords and ensuring that they have strong password security across all of their devices is one of the simplest, yet usually overlooked, ways for your employees to protect themselves when working from home. Sadly, hackers know that exploiting human mistakes is simpler than trying to get past a sophisticated security system, so they will try to break account passwords in order to access confidential corporate information. Passwords may be cracked by attackers using a number of techniques. For example, they will compile lists of often-used passwords that may be exploited to quickly access accounts with weak security. Another common and risky practice used by fraudsters is using repeat passwords. After they discover the password to one account, they will try to use it to log into other accounts. Employees who reuse passwords, especially across personal and professional accounts, are more likely to fall victim to a hack.
- The act of transferring files without encryption: Organizations may consider encrypting data that is kept on their network, but they might not think to encrypt data that is being transferred from one location to another. Your organization cannot afford to let this information remain vulnerable to being stolen by a cybercriminal because your employees communicate so much sensitive information on a daily basis, including customer account information, files, and more. If confidential firm information is intercepted, it may result in theft, ransomware attacks, identity fraud, and other problems.
- Misconfigured clouds: Notwithstanding its drawbacks, the cloud is an essential tool for distant work. One such danger is posed by configuration errors, particularly those that concern access. Businesses may unintentionally provide users with excessive access or neglect to put access restrictions in place.
- Webcam piracy: While working from home, staff members commonly take part in teleconferences and video chats that call for the use of a webcam. Sadly, crafty online crooks quickly and unlawfully access their cameras, invading their privacy. Even worse, if they leave sensitive paperwork lying around the office, trespassers may be able to see it by seizing control of their webcam.
- Threats are everywhere: Security concerns for remote work are prevalent. The move to remote employment is advantageous for nefarious insiders. Nowadays, sensitive data may be readily taken from a business computer through USB in the comfort of one's own home. Individuals nearby might potentially pose a hazard. While most of us believe that the individuals we live with are trustworthy, from the perspective of the firm, the staff residences are places where there can be no trust. Private conversations now be overheard, and displays and monitors in living rooms throughout the world display intellectual property.
10 Best Practices for Remote Work Access Security
The following is a list of some of the best practices you can use to improve remote access security in your company:
- Regular Security Updates and Patching
- Identity Access and Management
- Data Encryption
- Cybersecurity Training and Awareness Program
- Endpoint Security
- Firewall
- Security Policies
- Password Management and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Network Segmentation
- Using Virtual Private Networks
1. Regular Security Updates and Patching
To make sure that your systems don't have any unpatched vulnerabilities or weak spots, regular software upgrades are crucial. Cybercriminals are always looking for security flaws and gaps to expose and steal your sensitive data.
The integrity and security of your data may suffer irreparable long-term consequences if security patches and upgrades are ignored for a sufficient amount of time. Not only can timely fixes and updates eliminate security risks, but they improve application performance.
2. Identity Access and Management
Solutions for identity and access management are used to control user access rights, permissions, and privileges. In complex corporate contexts, IAM is a particularly useful tool since it makes sure that all organizational resources have the right and required degree of access control. Secure board portals, for instance, can be used by senior leadership to centrally store key papers and reports.
Modern remote policies and sophisticated security standards are the two key elements that improve the organization's security prospects in the current threat environment and help it comply with regulatory obligations.
IAM helps you firmly restrict access to apps, networks, and systems, which is crucial to attaining these security objectives. IAM, therefore, proves to be a bare minimum requirement in the modern digital environment.
3. Data Encryption
A great practice in terms of security is data encryption. Nevertheless, it becomes increasingly important when workers work remotely because of the possibility that gadgets may be stolen when utilized outside of a business environment or that private information could be accessed while being transmitted over the internet.
To that end, make sure that any data transferred over the network between computers controlled by the business and distant work sites is encrypted. Having staff use VPNs, which come with built-in encryption, to access remote systems is an easy way to do this. It's crucial to make sure remote-access tools, such as RDP clients, are current because out-of-date clients could not automatically encrypt data.
4. Cybersecurity Training and Awareness Program
Depending solely on security tools and procedures to guard your business against cyberattacks isn't always adequate. The integrity and security of your systems and applications will always be at risk due to rookie and unskilled users, regardless of how much money you invest in security solutions. Hackers now use phishing attacks and social engineering techniques to seriously harm businesses. Human error is mostly to blame for the effectiveness of these attacks. Consequently, it's essential to include security awareness training to raise awareness among staff members and promote a culture of safety and risk minimization.
5. Endpoint Security
System administrators need to increase endpoint security and have access to complete endpoint data at all times. Deploying a full endpoint detection and response (EDR) solution is advised in order to avoid next-generation malware, and data leakage, act swiftly in the face of attacks, and automatically manage software distribution and patching.
6. Firewall
A firewall will stop illegal access to and from the network, enhancing the security of the devices used by your employees. Firewalls monitor network traffic while detecting and preventing unauthorized traffic. Firewalls are crucial tools for defending your remote endpoints from a variety of online attacks.
Zenarmor next-generation firewall is one of the finest security tools for providing a secure remote access.
This enterprise-class, enterprise-strength content filtering engine detects and blocks advanced malware and threats. Even an ancient PC or a virtual system in your home lab can run Zenarmor! Liberated, light, and agile. This enables businesses to activate software-based micro firewalls on demand to effortlessly secure assets regardless of their location or time. A cloud-based web categorization database powered by AI classifies hundreds of millions of websites in real time. Unknown locations are categorized as five minutes.
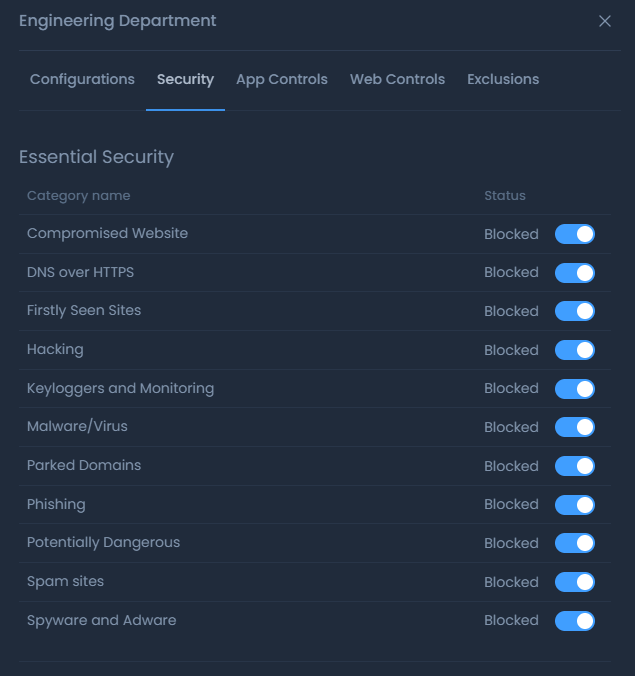
Figure 1. Configuration of Security Rules on Zenarmor
On the Security page of Zenarmor's website, you can establish general principles for threat analysis. The engine processes your SVN Cloud query requests in real time and determines whether they will be permitted or denied. It searches more than 300 million websites across 120+ categories in milliseconds.
Cloud Threat Intelligence data is queried in real-time whenever a device on your network attempts to connect to the internet. It allows us to respond in real time to wireless and malware outbreaks.
When a device on your network attempts to connect to any site on the internet, the Cloud Threat Intelligence database is queried in real time. It enables us to respond in real-time to malware and wireless outbreaks.
In the Free Edition, only the Essential Security options are accessible. Home, SOHO, and Premium Zenarmor Premium Subscriptions offer sophisticated security features.
Advanced Threat Protection is provided by barring websites that are known to host malware, infections, and deceptive attacks. Advanced Threat Protection from Sunny Valley provides commercial-grade protection and surveillance in near-real time.
How to Provide Secure Remote Access Using Zenarmor?
The main steps for safeguarding your remote employees against cyber threats using Zenarmor are outlined below:
1. Install and Configure a VPN Service
To allow your remote workers to access your corporate network and to provide internet access behind the company firewall securely, you must install and configure a VPN service. For example, you may install WireGuard VPN server on a OPNsense firewall by following the steps given in this article.
If you have a Linux firewall, reading the WireGuard Installation Tutorial written by Sunny Valley Networks may be helpful.
2. Install Zenarmor
The installation of Zenarmor is straightforward and you can install it on your OPNsense firewall via web UI quickly by following instructions given in the official documentation.
If you have a Linux-based firewall, you can install Zenarmor by running the one-liner command easily.
3. Complete Zenarmor Initial Configuration
To finish the Zenarmor installation you should complete the initial configuration on OPNsense GUI for OPNsense firewall or Cloud Management Portal for all platforms.
To be able to safeguard your VPN clients, you must select your VPN interface, such as wg0 for WireGuard, to protect during initial configuration.
4. Define a Policy
Finally, you should define a policy to start to protect remote workers via either OPNsense web GUI for OPNsense firewall or Cloud Management Portal for all platforms. You may protect your VPN tunnel interface by configuring the Default policy on Zenarmor Free Edition for free. You can add more policies on Premium editions.
Here is a video about how you can take take advantage of your Zenarmor NGFW regardless of where you are or which network you are connected to, by using Zerotier.
7. Security Policies
But how can you safeguard your company's confidential information when you have limited control over the devices connecting to your network? Where should you begin to ensure the security of your remote workforce? How may cybersecurity concerns associated with remote employment be lessened?
Creating a security policy expressly for remote employees is the first step. A company's written plan that outlines all standards and procedures for each employee who performs their duties outside of the company's physical offices is known as a remote work security policy. All significant facets of internet security are frequently covered by these rules. So let's focus on a few of the crucial security provisions that need to be in your remote work policy:
- Specify in detail which roles are appropriate for remote work: Be open and honest with your staff. Due to security concerns, everyone should be informed of which job duties may be performed remotely and which cannot. Sadly, not all jobs lend themselves well to remote work. The likelihood is that your work-from-home approvals will be viewed as unfair if you don't have a clear policy in place.
- Describe the instruments and platforms they should employ: Your on-site and remote staff should always be working together and using the same approved technologies, such as cloud storage services, tools for communication and video conferencing, and tools for project management.
- Provide staff members with instructions on what to do in the event that an account is compromised: They should be given explicit instructions on what to do if they think the company's data has been hacked, including where to report the event and when to change their passwords, among other things. These instructions ought to be covered in their required cybersecurity training along with other things like how to make good passwords.
8. Password Management and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Your remote employees' accounts will benefit from an additional degree of protection provided by multi-factor authentication. The likelihood of cybercriminals accessing your critical systems decreases with increased security measures.
In addition to adopting multi-factor authentication, your staff members ought to use a password manager. They won't have to keep track of all the many passwords they need to create for their work-related accounts if they do it this way.
9. Network Segmentation
By reducing the attack surface to many layers and thwarting lateral network attacks, network segmentation reduces security concerns. Because of this, even if an attacker manages to get past your initial line of security, they are limited to the network segment they access. When your network is separated into neat sections, it is easier to pinpoint problems and spot threats right away.
10. Using Virtual Private Networks
When your employees access unsecured networks, such as Wi-Fi hotspots, they still need a VPN connection, even if they work from home. It is advised that your staff members use the VPN provided by your business. This technology helps to increase security by routing traffic from your company's private network across the internet. In essence, anyone attempting to read the encrypted data will be unable to do so. And in doing so, they will be able to access your company's intranet, a secret network created only for use by workers (if you have one).
What is the Relationship Between ZTNA and Secure Remote Access?
As borders blur and the number of users who want access to resources grows, cybersecurity and IT teams are aware that concepts like perimeter and trust are swiftly losing their relevance. Organizations no longer have a firewall moat and four castle walls to keep away intruders. Nowadays, a lot of security teams use the zero-trust network access(ZTNA) principle. Never trust, always verify is the foundation of a zero-trust approach. Continuous verification, a zero-trust alternative to perimeter security, is a crucial part of protecting a remote workforce dependent on the cloud.
Which is Better for Secure Remote Access? ZTNA or VPN?
While both VPNs and ZTNA solutions provide secure remote access, there are some significant distinctions between the two that may influence your choice of solution. The following are a few of the most significant distinctions between a VPN and ZTNA:
- Trust And Access: The fact that ZTNA was established on the tenet of "never trust; always verify" is one of the key distinctions between VPNs and ZTNA solutions. When a person or device connects to the corporate network, VPNs presume that they can be trusted. Once validated at the beginning of their sessions, these trustworthy users and devices are given unrestricted access to the whole network. This indicates that an attacker can get access to the whole internal network using a compromised device or user account by skipping just one round of authentication. On the other hand, ZTNA divides up network resources according to the applications they are used for, and it only permits users to access the specific apps that their credentials enable them to utilize. The ZTNA solution performs user and device authentication each time a request is made to access a new area of the network. This makes it considerably more difficult for attackers to obtain access to the network in the first place and significantly reduces the amount of harm they might cause even if they did.
- Visibility: IT or security administrators cannot see which apps the user has signed in to or for how long when a user connects to the network using a VPN; they can only see that the user has visited the network and when. ZTNA solutions' micro-segmentation enables administrators to see which apps users are visiting in real-time. This offers two advantages. First off, it enables administrators to rapidly see any unusual behavior that would point to account penetration, such as a person using a program they wouldn't otherwise use. Second, it helps administrators determine whether they have paid for any programs that aren't utilized or are used by fewer users than they anticipated, helping them to save money on unused subscriptions.
- Speed: Latency in the connection might occur because VPNs send traffic across several servers before passing through a central location in the corporate data center. Yet, ZTNA solutions link users to apps directly without requiring data transmission through that hub, reducing latency.
- Ease Of Use: Businesses must download and configure a VPN client on each user's device in order to enable access over a VPN. Once installed, VPNs frequently include integrated single sign-on (SSO) to streamline access control and provide users with a simple login process. They have long been quite popular among businesses that want to allow workers to work remotely for a brief period of time, such as when traveling on business or juggling personal commitments. Nevertheless, VPNs can be troublesome for long-term remote access since end users have to remember to log in to the VPN client every time they need to access network resources. ZTNA solutions are initially a little more difficult to implement than a VPN, but once properly set, they operate in the background, silently allowing users to use the programs they require after authenticating themselves. Remote employees can safely access the corporate network via ZTNA solutions and VPNs, but they do so in very different ways. ZTNA is frequently viewed as a safer, more user-friendly version of the VPN, but VPNs continue to serve a purpose by protecting users from endpoint and online dangers that may be accessed through untrusted Wi-Fi networks and unmanaged devices. For smaller companies with fewer workers who work remotely or whose employees don't always work remotely, we advise a VPN service. On the other hand, ZTNA solutions are a fantastic choice for bigger businesses or those with a significant proportion of remote or hybrid workers. They are especially well suited for enterprises that seek to build a zero-trust architecture because, once set up, they are simpler for end users to use than a regular VPN, and they offer secure, least privileged access to corporate resources.
What is the Relationship Between SD-WAN and Secure Remote Access?
Wide area networks are essential components of dispersed companies because they link the main office, satellite offices, cloud services, and users in various places. Yet managing them may be difficult, expensive, and time-consuming. Depending on their architecture, WANs can potentially reduce performance and traffic, and they pose a number of security risks.
Via the provision of a network overlay that enables IT to remotely set up, administer, monitor, and protect the majority of WANs, including edge devices and remote employees, software-defined WANs(SD-WAN) can assist enterprises in overcoming the difficulties associated with traditional WANs.
What is the Relationship Between SASE and Secure Remote Access?
A new idea called Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) integrates network and security operations into a single cloud service to reduce the amount of traffic that must pass through data centers and to support remote workers, IoT adoption, and cloud-based application use. Using a SASE framework, businesses may connect remote users while maintaining edge-to-edge security, avoiding bottlenecks, and enhancing speed.
What is the Relationship Between Cloud Security and Secure Remote Access?
The cloud is essential for managing a remote workforce since it allows users to access resources from anywhere. Access to the cloud may boost efficiency, teamwork, and employee happiness, but clouds present security issues that need to be resolved. Cloud use must be addressed with adequate planning, security measures, and best practices in place to prevent unique cloud security risks and cloud vulnerabilities, even if it is essential for enabling cybersecurity teams to monitor remote access with adaptive strategies, rules, and tools.
What are the Best Secure Remote Access Tools?
Due to their outstanding customer satisfaction ratings, the following secure remote access tools received a top-rated recognition:
- Splashtop
- GoToMyPC
- Rescue
- Central
- TeamViewer