Digital Rights Management in Digital World
The world's appetite for content may now be satisfied almost instantly. You may now watch or listen to practically anything, at any time, on any device. And you can have it delivered to you almost instantly. Meanwhile, as digital media businesses get unparalleled insight into market segmentation through business intelligence analytics, and internet speeds continue to improve, it is allowing content providers to establish unique and personalized ways to cater to a worldwide audience.
People, on the other hand, rarely want to pay for something they can obtain for free. Piracy of intellectual content has become one of the most serious threats to the creative industries, whether for personal gain or because they simply don't care about infringing copyright rules. A flexible and effective solution is required to safeguard digital information, which is where digital rights management solutions come in.
The era of digital content distribution has the potential to be highly profitable, but it is challenged by content piracy and unlawful access.
The goal of digital rights management is to secure digital content and the revenue associated with it for rights holders.
Throughout this article, we will go over what digital rights management (DRM) is, how DRM works, the purpose of DRM, the benefits of digital rights management, the 4 types of digital rights management, the most common digital rights management use cases, and the best practices for DRM. And we will also talk about the best digital rights management software for DRM and what features DRM software should have.
What is Digital Rights Management?
The use of technology to limit and manage access to intellectual material is known as digital rights management (DRM). Another definition of DRM is transferring control of digital content from the person who owns it to a computer program. By preventing the unlawful distribution and modification of information, DRM strives to safeguard the rights of the copyright holder.
Digital rights management (DRM) is a method of protecting digital media copyrights. This strategy entails the deployment of technologies that restrict the copying and use of copyrighted content as well as proprietary software.
Digital rights management, in some ways, permits publishers or authors to regulate what paying users can do with their works. Implementing digital rights management solutions or processes for businesses can assist in preventing people from accessing or utilizing specific assets, allowing the firm to avoid legal concerns that arise from unlawful usage. DRM is now playing an increasingly important role in data security.
DRM allows authors, musicians, filmmakers, and other content providers to specify and regulate what their content can and cannot do. DRM enables them to safeguard their copyrighted information, protect the creative and financial investment they have made in their work, and make it difficult for their media to be stolen or illegally shared. They can, for example, block users from accessing specific assets in order to avoid any legal concerns that may arise from illicit usage. This is critical for copyright and intellectual property protection.
How Does DRM Work?
DRM usually entails the use of codes that prevent content copying or limit the number of devices through which a product may be accessed. Content providers utilize apps to limit what users can do with their material or to encrypt digital media, which can then be viewed only by those who have the decryption key.
DRM accomplishes its main goals, data protection, and governance, in four different ways:
-
Encryption: To prevent illegal use and copying, valuable content is encrypted.
-
Governance: In order to use the encryption key, a number of requirements must be satisfied.
-
Authentication: When a user is confirmed to comply with these conditions, their DRM client is given permission to encrypt the content.
-
Enforcement: The user's authorization is periodically examined to make sure they continue to adhere to the license's conditions.
Here's a high-level overview of how DRM technology works:
-
Digital content is encrypted as part of the "packaging" process and can be unlocked only with a secret encryption key.
-
This key comes with a digital license that specifies how to use the content.
-
When a user seeks to view the content (for example, by clicking on a show to watch), the DRM client validates the license.
-
If satisfied, the user receives a validation token.
-
This token notifies the receiving device that content decryption is permitted.
-
Even while copyright laws apply to digital content, it can be difficult to keep an eye out for illicit activities online. DRM prevents digital content from being stolen in the first place by putting up hurdles to doing so.
There are numerous ways to safeguard your program, product, or content. For example, you are able to:
-
Set a deadline by which the user will no longer be able to access your document or material. Limiting a user's ability to use something is another way to do this. For instance, if the user has listened 10 times or opened and printed the PDF twenty times, the document may be canceled.
-
Only allow access to specific IP addresses, places, or devices. In other words, if your media is exclusively accessible to US citizens, it won't be available to people in other nations.
-
To confirm ownership and identification, watermark pieces of art and documents.
-
Publishers and authors can also access a log of the individuals and times at which specific media, content, or software was utilized thanks to digital rights management. For instance, you can know who accessed an e-book and when it was downloaded or printed.
What is the Purpose of DRM?
DRM's declared goals are to stop piracy and safeguard intellectual property. Copyright holders can avoid intellectual property theft and copyright infringement, maintain artistic control, and guarantee ongoing cash streams by placing restrictions on what the owner can and cannot do with their product. By limiting usage, DRM can assist in ensuring owner safety.
DRM is used by owners of copyrights for less ethical motives as well. DRM prevents rivals from enhancing the product. It renders products incompatible with one another, obliging owners to purchase only complementary goods, to the copyright holder's advantage. When the DRM scheme changes, it compels owners to upgrade to the most recent version. DRM generates income by preventing owners from copying, selling, giving away, repairing, or altering their products. Actually, data governance and data protection are digital rights management's two main goals.
What are the Benefits of Digital Rights Management?
Digital rights management systems allow you to share data/files while maintaining control over who has access and what they can do. Secure file collaboration and the need to share files containing sensitive information with third parties is a requirement for businesses of all sizes and industries. The advantages of DRM are explained below:
-
DRM helps to enforce copyright laws: Even if you identify an image as "not for commercial use", search engines make it available to every PC owner on the planet. Even if the image is copy-protected, someone may snap a screenshot and embed it without the necessary attribution/payment. Watermarking is a DRM technology that enforces copyright rules in real-world use cases.
-
DRM helps monetize digital content more effectively: DRM aids in the more effective monetization of digital material. The widespread piracy of digital content significantly impedes monetization. Users are prone to prefer free access, even if it is unethical unless suitable checks and balances are in place. Today, OTT platforms ensure that practically every consumer on the planet can get their desired content in an ethical manner. And DRM contributes to this. Another significant advantage is the ability to restrict content to certain audiences, such as age-specific content consumption or consumption in accordance with regional censorship regulations.
-
DRM is directly linked to your business growth: DRM prohibits competitors from obtaining sensitive information or intellectual property. Take, for example, a pharmaceutical company. It may be working on a patent for a revolutionary new cure was granted, but the lack of DRM mechanisms could lead to a competitor purchasing the IP and bringing it to market sooner. Alternatively, a bank undertaking an internal inquiry may have critical documents made public, harming its market reputation. Enterprise content management with DRM mitigates such dangers.
-
DRM maintains your right to ownership: DRM is critical in assisting authors and writers in protecting their work. They can employ technology to protect their content and prevent others from modifying or rebranding it as their own. While consumer-facing multimedia content is easier to classify in terms of ownership, scientific, technical, and industry-specific content assets necessitate a clear stamp of ownership as well as a controlled channel of distribution to assure correct usage.
-
DRM raises awareness: Users in the digital age can grow desensitized to issues such as content ownership, money generation, and access accountability. The physical constraints that naturally exist when borrowing a book from a library and making one or two photocopies no longer apply. It would only take a few minutes for a user to extract a thoroughly researched essay from a pirated eBook and distribute it publicly on their personal website. When users are confronted with DRM restrictions, they obtain much-needed knowledge of author rights and fair usage regulations.
-
DRM aids in compliance with regional laws: Regulations may specify that users can only open a file in a certain location. Governments, government organizations, and government contractors are largely affected. Some DRM techniques restrict how and where a user opens a file; you might even combine this with device-specific DRM to reduce the risk of non-compliance even further.
-
DRM simplifies third-party partnerships: Data security is one of the most important issues when forming a third-party collaboration. There is always the worry that the partner would disregard internal data security best practices and jeopardize your trade secrets. According to a study, 53% of firms have had a data breach caused by a third party, with an average cost of $7.5 million. DRM eliminates this danger, allowing you to form meaningful partnerships without having to worry about data security.
-
DRM supports better licensing agreements and technology: DRM contributes to improved license arrangements and technology. The goal of digital rights management systems is to limit how consumers interact with content, such as listening to music on different devices or sharing content with friends and family. Users who do not wish to be restricted by DRM codes can help vendors who offer and sell DRM-free products. DRM-free content encourages vendors to explore alternative licensing technologies to DRM.
-
DRM provides Income protection: Creating, filming, and editing documentaries, movies, and other media take money, and artists aim to recoup their investment by selling their work for a profit. They may lose money if that content is leaked or shared without their permission. Content publishers restrict access to their videos to paying customers only.
-
DRM offers Intellectual property education: Many people are unconcerned about the copyright details of the content they own. DRM enables firms to properly express to customers what they can and cannot do with their digital products, thereby educating users on how intellectual property works.
-
DRM protects confidential information: DRM technology can assist firms in securing sensitive documents ranging from contracts and strategic plans to sensitive personal data. It enables them to manage and trace file access while also preventing files from being edited, saved, duplicated, or printed.
-
DRM avoids legal issues: DRM technology assists content purchasers in adhering to the licensing information that governs how, when, and even where the content can be used and avoiding financial penalties.
-
DRM provides revenue recovery: Digital rights management helps secure revenue streams. Video and moviemakers spend money to create their films in the expectation of recouping their investments once they hit the big screen, or when they stream or are distributed online. DRM can assist in ensuring that only paying users can view a video or movie. It also ensures that the video is only visible to a certain group of people. Adult-oriented content, for example, should be restricted to people who can prove their age.
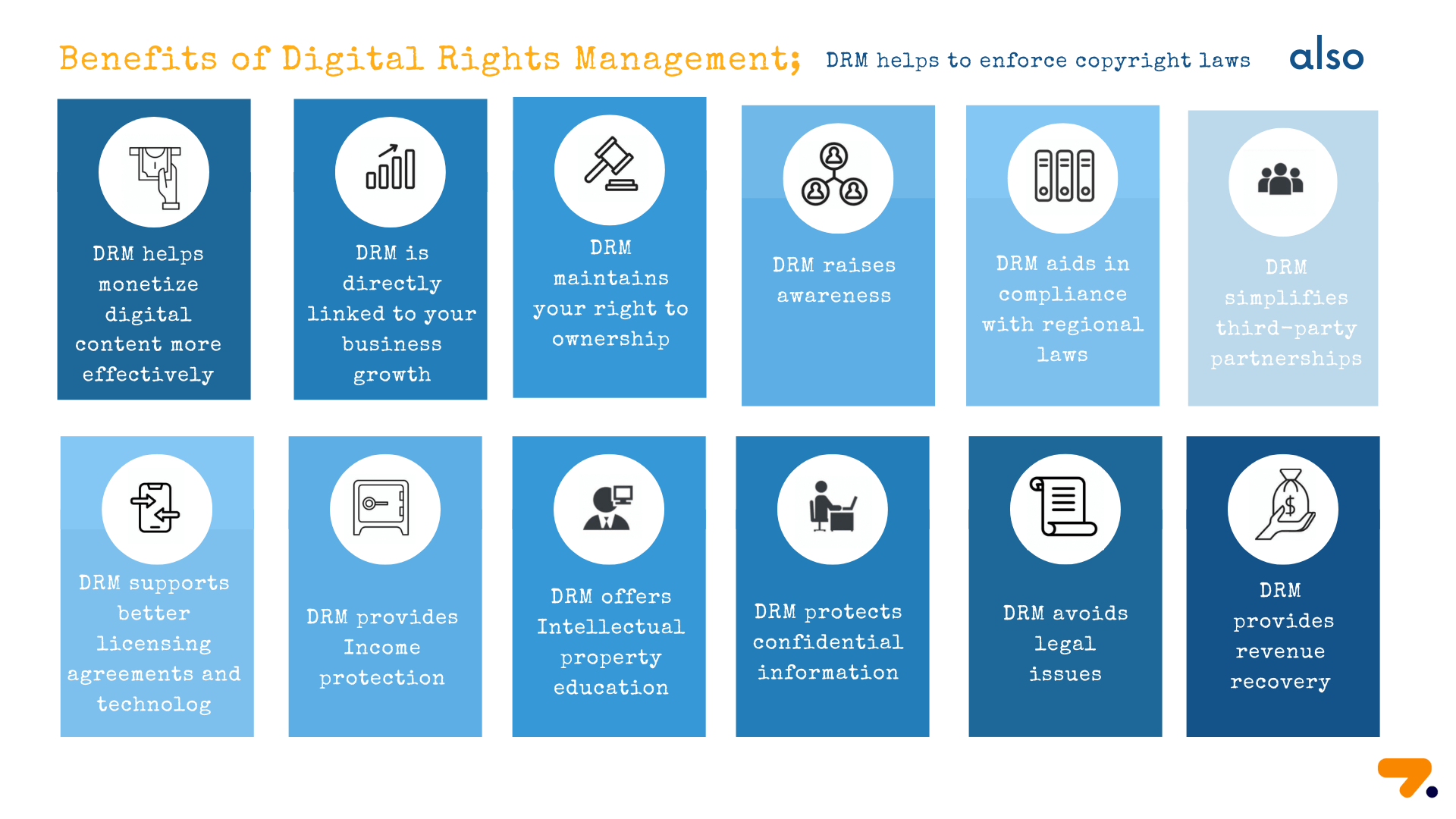
Figure 1. Benefits of Digital Rights Management
What are the Four Types of Digital Rights Management?
DRM technology is found on a wide variety of digital assets, including films, music, and ebooks, as well as proprietary company information, database subscriptions, and software. These works' creators are interested in DRM not simply to prevent unlawful copying, but also to prevent individuals from modifying or utilizing their works in ways they did not intend.
There are many ways to protect your content, software, or products. And the most common types of digital rights management are as follows:
-
DRM restricts or prevents users from editing or saving your content.
-
DRM restricts or prevents users from sharing or forwarding your product or content.
-
DRM restricts or prevents, users from printing your content. For some, the document or artwork is only printed up to a limited number of times.
-
DRM disallows users from creating screenshots or screen grabs of your content.
What are the Most Common Digital Rights Management Use Cases?
Digital rights management is becoming increasingly crucial in today's digital environment, not just for digital content creators but also for businesses and individuals who use digital assets licensed or purchased from third-party creators. Here are a few examples of common digital rights management applications:
-
Limit Access to Files: DRM technology is used by many firms to protect business-critical documents or sensitive information, such as confidential employee data, business plans, and contracts. DRM allows enterprises to track who has accessed their files, regulate access to them, and manage how others can use them. It also stops files from being changed, duplicated, saved, or printed.
-
Keep Your Digital Work Unaltered: Digital rights management ensures that digital work is not altered in any way. Creators frequently want their work to be distributed in its original form in order for it to accomplish its intended purpose. For example, the FDIC (Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation) employs digital rights management to prevent unlawful redistribution of critical digital material.
-
Prevent Leaking Confidential Information: Companies can use digital rights management to control access to sensitive information. They can utilize these technologies to limit access to sensitive data while allowing it to be safely shared. Having DRM technologies makes it easier for auditors to analyze and discover leakage. In a commercial setting, digital rights management is referred to as information rights management or enterprise rights management. DRM is used by healthcare organizations and financial services firms to comply with data protection standards.
-
Prevent Software Tampering: According to a DataProt survey, 57% of computer users have pirated software in the past. It is critical for technology companies to secure their valuable software products against piracy in the age of software-as-a-service (SaaS). As a result of this concern, digital rights management is critical for preventing software misuse. Microsoft customers, for example, must obtain a personal user license and enter their unique key before installing any Windows or Office program on their own computer.
-
Produce Content Safely: Authors, singers, film professionals, and other content creators can employ digital rights management to prevent unlawful usage of their work. It can help protect companies' bottom lines and govern product distribution. DRM also safeguards the creative output associated with brands. Because having a consistent brand image is crucial to corporate success, misusing a company's logo or campaign materials may be immensely detrimental.
What are the Best Practices for DRM?
There are many DRM implementation strategies, and efforts to create new ones are ongoing. Many DRM techniques use encryption or computer code that is incorporated into digital content to restrict access or use. The best practices for DRM implementation are explained below:
-
Maximize investments using free digital rights management tools: It's a prevalent fallacy that the only DRM systems that can guard your content against unethical use are the priciest or most premium ones. Asking staff to password-protect every document can be just as successful at limiting distribution using paid DRM products or already-existing technologies like MS Word. In reality, DRM is as much a mindset as it is about technology. For digital rights management, you can make use of a number of free programs, including Drumlin Publishing and InstallAware. With InstallAware, you can safeguard your apps without altering their source code. A PDF security program called Drumlin enables you to define permissions and add watermarks to PDF files.
-
Build a content selection framework before implementing DRM: DRM is not required for every content. In some circumstances, DRM controls actually prohibit your material from obtaining the amount of reach and engagement that you desire. For this reason, a system for content selection must be in place before DRM is implemented. A small-scale production company, for instance, might decide to utilize DRM for a new film but not for its trailer. DRM mechanisms used carelessly will prevent shareability. Think about creating a diversity and inclusion presentation deck. You want the deck to be seen by as many individuals within and outside of your business as you can. A complicated DRM solution like passwords or device-based verification would just get in the way of the social media chatter, engagement, and reach that you want. When choosing content for DRM, consider the following questions:
- Is it monetizable or will it help me monetize?
- Is it monetizable or will it help a rival monetize?
- Could unchecked distribution violate regional, industrial, or internal rules?
-
Integrate with other data management infrastructure: Like most technologies, DRM functions best when combined with complementary tools like content management systems (CMS), digital asset management (DAM), and data loss prevention (DLP). In order to avoid potential data loss or leakage, a DLP technology will restrict data exchange under certain circumstances. This can be coupled with DRM to ensure that the protocols are followed when exchanging data within your DLP ambit. Having a designated "data owner" in place who handles data loss, rights management, and the usage and distribution plan generally is one of the best practices to adhere to. This owner may be a single senior management stakeholder, a team formed especially to monitor secure data or content use, or even an outside expert who has years of experience in data management best practices. However, integrating DRM with the other elements of your technology stack is the first step in realizing the benefits of this unified view and administration.
-
Make room for scalability and flexibility as the landscape evolves: Your approach to digital rights management must change in step with the sophistication of content formats, delivery methods, and DRM solutions. Your DRM should also be flexible enough to accommodate new business models and business growth. A research organization would desire to go from static content assets to dynamic/topical content reports, to give a straightforward example. In contrast to the former, the latter will need a whole different DRM solution, such as time-bound decryption keys. According to this best practice, businesses must investigate cutting-edge DRM technologies like point-to-point encryption and blockchain in order to remain ahead of dishonest competitors. The seamless authentication of high-definition video material without online connectivity is made possible by point-to-point protection, retaining the user experience for the consumer. Considering its transparency and immutability, blockchain is yet another fascinating DRM technology. For instance, IP DRM blockchain technology is already being developed by the tech and media company Sony. Be sure to learn from your errors when it comes to DRM. Companies must adapt as employee expectations change in various working styles and customer attitudes toward digital content change. Productivity and interesting experiences shouldn't be hindered by DRM. Fortunately, the billion-dollar market of today provides you with the necessary DRM tools and services to accomplish this at the most cost-effective prices.
-
Conduct company-wide surveys to obtain user buy-in: Data Exchange Security Prioritizes Data Exchange Security over Access Control. As a result, it is crucial to win over and receive active support from your intended user base, your employees. Inefficient DRM will eventually cause bottlenecks in content sharing and may even call for a costly DRM redesign. As a general guideline, create focus groups with individuals from the enterprise's key content audiences. With this focus group, experiment with several DRM scenarios while performing thorough surveys to evaluate their quality of experience and potential productivity consequences. Once you have a workable implementation plan for DRM in place, do a quick company-wide poll to gauge employee satisfaction. It is vital to review your DRM strategies as soon as possible if you are unable to win over a substantial user base.
-
Divide the compliance burden between users and IT: Increased enterprise risk results from putting all of the responsibility for DRM compliance on users. The DRM strategies we outlined impose limitations on how staff members use and share content, but they also serve to increase awareness. Employees might find ways around the limitations and weaken its effects if they are unaware of what Digital Rights Management is and why it is so vital (e.g., sharing document passwords with a family member). Divide the compliance burden between users and your IT department as a result. IT can take responsibility for enforcing DRM across the user base by integrating it into its bigger framework of IT policies. The organization as a whole and IT are both responsible for the actions of employees.
-
Be mindful of the downsides of digital rights management: True, DRM is criticized by some. One argument says that DRM violates the fundamental ownership rights of someone who has lawfully purchased content. Let's say you bought an eBook; you might argue that you should be able to read it on any device you want. Less philosophically speaking, complicated DRM operations might degrade the user experience, discourage usage, and even force users to transfer to a rival platform. To solve these drawbacks and match UX expectations with the DRM technology architecture, businesses should undertake surveys.
-
Minimize shadow IT and unmapped distribution channels: Data owners have always had a tough time tracking data sharing and usage across these covert channels due to shadow IT. Your DRM burden can be somewhat lessened by preventing shadow IT. Shadow IT is a major issue for practically every large-to-mid-sized organization because so many of us work from home. Employees commonly use their personal devices for work and download SaaS applications that do not adhere to the IT policies of the company. These channels are used for file, document, and data sharing, which is considered "shadow IT" and is challenging to regulate. Shadow IT reduction will lower your DRM loads, assisting in the proper allocation of your capital.
What are the Top Digital Rights Management Software?
Digital rights management (DRM) software provides customers with a variety of features meant to preserve their content and guarantee it is viewed within their designated restrictions. Businesses are continually sharing files internally and internationally, and many others exchange branded assets or host media files often. Business content that is shared or hosted is protected by DRM solutions, which guarantee that it is only utilized for its intended purposes. For shared documents, DRM software can offer features like watermarking and timed expiration, and for media assets, subscription and license management. Secure file transfers are frequently made possible by DRM solutions that make use of built-in encryption software.
Many digital asset management software solutions contain full-fledged DRM inside their solutions to ensure branded assets are distributed safely and serve enterprises in diverse industries around the globe.
The best Digital rights management (DRM) tools are explained below:
-
Bynder: Bynder is the greatest DRM software available. It is a cloud-based digital asset management program that enables a team to communicate. Bynder makes it simple and quick to deliver content to the market. Teams use this DRM software to interact in real-time, make collaborative adjustments, and approve content. It simplifies the management of digital files. Furthermore, Bynder includes a slew of other capabilities, such as auto-formatting for file kinds and channels, simple file storage and sharing, and more. It has powerful DRM capabilities. This DRM software is appropriate for video/eBook/PDF files. Some features of the Bynder are as follows:
- Bynder allows you to lock sensitive items that require extra security.
- It sends out automated notifications about content limitations.
- Access can be restricted by downloading approval functionality.
- The DAM from Bynder is simple to use.
- Bynder is used by Puma, Scotch and Soda, Siemens Healthineers, and Tata Steel, among the top brands that use Bynder.
-
CapLinked: CapLinked is a comprehensive DRM platform for sharing business-related files and documents that is web-based. CapLinked is excellent for midsize and enterprise businesses such as real estate, aerospace, energy, finance, legal, and so on. It serves as a central repository for enterprises to store and distribute sensitive information. Companies can assign various document access permissions and create custom groups to upload, download, modify, and view documents. Some features of the CapLinked are given below:
- Document access can be granted with permission.
- Documents can be locked for a specified area.
- Analytics in real-time and activity tracking.
- SSL encryption uses a 256-bit key. Customers of CapLinked include Goldman Sachs, Thomson Reuters, KPMG, and Microsoft.
-
Digify: Digify has received numerous international accolades and has been featured in over 60 publications worldwide. It provides secure and safe virtual data rooms that are simple to set up and utilize. Digify is useful to businesses since it saves time and allows them to track and deliver business-related papers to investors, clients, and partners. Digify is HIPPA compliant and provides a variety of digital rights management options, which is a considerable advantage. Some features of the CapLinked are as follows:
- Admin role permissions, file index enablement, and access terms.
- File tracking, automated watermarking, and document security are all available.
- Upload files directly from your PC or cloud storage. Digify customers include Comcast, Harvard Medical School, and LinkedIn.
-
MemberSpace: MemberSpace is a great DRM solution for monetizing and protecting web content. MemberSpace lets you quickly lock access to any web page with MemberSpace, create memberships for member directories, video lessons, courses, and more, and control the web pages as you see fit. You will only need to establish the fee for examining the content and web pages of your website, and MemberSpace will handle the rest. Some features of the CapLinked are as follows:
- The user interface of MemberSpace is simple to grasp.
- MemberSpace's customer service is excellent.
- There is no requirement to use a certain CMS.
- There are services for currency, taxation, and invoicing. Top MemberSpace Customers Include: Visual Media Church, Ladies of Real Estate, and multiple small businesses.
-
Primetime DRM by Adobe: Adobe Primetime DRM functions as digital rights management software and includes a variety of features such as subscription management, licensing management, video and audio protection, and more. It protects all types of material for Xbox, Roku, iOS, Windows, and Mac, including download-to-own, rental, subscription, and anonymous content. It is a cloud-based DRM program that works on a variety of devices. Some features of the CapLinked are as follows:
- Closed captioning is an option for videos.
- Dynamic ad placement improves the ad experience of various live events.
- ML-based currency optimization is possible to reduce waste.
- It can aid in the authentication of various device content. Customers of Primetime DRM include Star TV, NBC, and Comcast.
-
Red Points: Red Points is a DRM technology that assists businesses in monetizing/claiming content rights, preventing online piracy, eliminating counterfeit products, and tracking dealers in order to safeguard the brand's future. By integrating monitoring services, distributor capabilities, and copyright enforcement, Red Points provides consumers with a clear view of any brand's internet presence. Furthermore, the DRM software allows clients to eliminate online counterfeit products from many sites, including eBay, Facebook, Amazon, and others. Some features of the CapLinked are as follows:
- Remove illegal content, follow-ups on violations, deindex requests, and automatic removal.
- Sellers in the partner network can be easily monitored.
- Examine online markets for counterfeit goods.
- Monetization of video across numerous social media platforms. Customers of Red Points include Farsali, XD Design, and Fila, to mention a few.
-
Vitrium Security: Vitrium Security is a dependable DRM platform that assists clients in safeguarding their content. It functions as a single platform, allowing you to view, control, and protect films, photographs, documents, and audio. Real-time analytics, user access controls, and data encryption are all included. Because of its simple interface, Vitrium Security is used by content owners all around the world. Furthermore, Vitrium Security allows users to safely post their material. Some features of the CapLinked are as follows:
- Safeguards sensitive, intellectual, and confidential data.
- AES encryption of 256 bits.
- Individuals who have been granted authority can access files.
- Manage groups, assign rights, and track user activity. Customers of Vitrium Security include Grand Canyon University, Aeris, and Title Vest.
-
Widevine: Widevine is an easy-to-use DRM software that enables clients to encrypt, securely distribute, and license playback content. This DRM software is perfect for digital media providers, numerous service operators, and content owners that want to ensure the continuity of their revenue-generating services. It functions as a comprehensive DRM software that allows you to protect video and audio files from piracy. Some features of the Widevine are listed below:
- Can secure several client devices and act in tandem.
- Provides an HTML5 player.
- The hardware-based trust, rendering, and decryption root.
- Support for concurrent access is provided. Widevine customers include LG, HBO, Facebook, Disney, Google Home, and Warner Bros.
Which Features of DRM Software Should Have?
There are several aspects to look for in a digital rights management (DRM) software solution. Here are some key features that every DRM software should have:
-
Control distribution of confidential documents: DRM solutions enable businesses to protect critical documents from being tampered with, leaked, or mistreated. DRMs let enterprises track who accessed files, regulate access to them, and manage how individuals use them. If any confidential information is accidentally released. DRM tools can look into what or who caused the leak.
-
Restrict and revoke access to your files: Authors, filmmakers, singers, and other content providers can employ DRM technology to prohibit unlawful use of their work. It protects their bottom line and ensures proper product distribution.
When, who, what, and when may all information regarding file access be tracked in modern DRM tools? You can limit the number of downloads and the duration of file access. Access Tracking is a common security request from clients asking for DRM technologies.
-
Track user activity with analytics: The DRM software should give you precise information on how the content is shared and distributed across various channels. Individual access records, editing attributions, precise timestamps, and other information should be displayed via the tracking and analytics tool. Furthermore, analytics should assist clients in determining which distribution channels are best.
Who Uses DRM Tools?
The following sectors use Digital rights management (DRM) solutions to save their assets:
-
Associations & Professional Training Organizations: You need to know how to share your priceless training videos with your members and learners, whether you work for an association or a professional training organization. Associations of all sizes and types may easily secure their priceless educational resources using DRM software, which also integrates with the association administration systems (AMS) or learning management systems (LMS) you already use.
Protect the eBooks, manuals, research papers, training videos, podcasts, and other supplemental materials that your association produces, and distributes through your LMS or AMS and set various access control rights, such as expiration dates and device restrictions so that only authorized members or customers who have paid for access can access the content. A good DRM solution will also safeguard files downloaded to a computer or shared drive and operate with today's read-aloud software for visually impaired people.
If you've already established a date limitation, access to the association's content, e-learning, and course materials will be immediately terminated when your membership or class expires. Your pupils will be able to finish their training, and you won't have to worry about whether or not they passed the information on to the next session.
-
Market Research & Data Intelligence: Market research takes countless hours in the commodities, oil and gas, medical, pharmaceutical, technology, and other business sectors. It would be a pity for those hours to become worthless when reports, videos, price sheets, forecasts, and more get leaked online or shared with those who haven't paid for the report or haven't registered for your service. It is critical that you use a digital rights management (DRM) solution to safeguard your valuable research data.
-
Financial Services: Asset management firms, hedge funds, insurance companies, private equity firms, and other investment management organizations must defend the interests of their clients, shareholders, and themselves. If the last decade's worth of data breaches has taught us anything, it's that unauthorized users will go to any length to obtain the information they seek. That is why it is critical to safeguard your content with the best DRM solution available.
Dropbox and data rooms simply safeguard the 'house' or 'portal' via which clients access the files; they do not protect individual files or documents once downloaded. A good DRM solution will safeguard the files when they are downloaded, regardless of where they are kept or saved. Allowing your content to be leaked or shared with others without authorization puts your reputation and financial line at danger.
-
Standards Organizations: Most people rely on their industry trade associations or national standards groups to keep them informed about the codes and standards that influence them in their business, region, or country. As a result, they are the businesses with the most up-to-date information that professionals require to stay in compliance and/or gain a competitive advantage. That is why firms and trade professionals pay membership fees and subscription dues to associations and trade organizations in order to have access to the standard papers or training materials they require to be successful.
It's crucial to protect the standards documents that you sell and to secure your association's revenue-generating content, otherwise, all of those fees and dues could come to a crashing halt. Your documents, videos, audio files, and other content must be encrypted so that only those who have paid for access, or your authorized users, can see them. Even if someone has a subscription, sharing, printing, and copying content could also be limited. When their membership expires, access should be revoked. These safeguards are the only way to ensure that your valuable content retains its value.
A DRM solution can be effective not just for locking down your content for specific audiences, but also for introducing additional multi-tiered subscription options as a strategy to boost revenue within your business. Charge a cheaper fee for view-only access to a standard document with a limit of one device and no printing, but raise the degree of access for a premium-paying subscriber - allow them to access the standard on more devices and print as much as they want. You will generate more revenue if you upsell your members or subscribers to the premium option.
-
Publishing & Media: Content is everything for professionals in the media and publishing industries. Protecting such content is critical to their bottom line. While they must share it with their subscribers, leaks, piracy, and unauthorized access render their membership fees null and void. Why pay for something that you can get for free? The same holds true for self-published authors.
Media and publishing organizations can utilize a quality DRM system to provide separate content and user controls for distinct groups of users. Similar to the analogy for standards organizations above, media and publishing companies can charge a lower fee for people to buy view-only access to their video or eBook content, content that can only be viewed on one device; for a higher, premium fee, they can access the content on multiple devices. Implementing a DRM solution does not have to be one-size-fits-all. It may be multifaceted and imaginative, allowing media and publishing companies to sell their revenue-generating material for even more than they anticipated.