Cryptanalysis in Cybersecurity
Cryptanalysis is the study of techniques for deciphering encrypted data without having access to the secret data typically needed to do so. With the help of cryptanalysis, it is possible to discover hidden data without resorting to brute force techniques, such as the encryption key. Cryptanalysis can also be used to describe the process of decrypting a message.
One of the most important tools in the field of cybersecurity is cryptanalysis. It is important to note that cryptanalysis is an ever-evolving science, as new encryption algorithms and technologies are produced and new ways for breaking encryption are discovered. Cryptanalysis is a vital tool for cybersecurity experts, as it enables them to detect and exploit vulnerabilities in encryption systems, as well as create and implement more secure encryption methods.
At the beginning of this article, we shall define cryptanalysis and discuss its techniques and varieties. In the following sections, we shall discuss the function of cryptanalysis in cybersecurity. Then, we will discuss who works in this field, how this field may be learned, the instruments used for cryptanalysis, and the subject's history.
What are the Cryptanalysis Techniques?
Cryptanalysis is the process of decrypting a cryptographic system or communication or uncovering its hidden meaning. There are several approaches that may be employed in cryptanalysis, such as:
-
Brute force: This requires attempting every key or character combination until the proper one is discovered. This approach is often only successful for very short or basic keys and can be highly time-consuming.
-
Frequency analysis: This includes determining the key or plaintext by studying the frequency of letters, words, or patterns in a ciphertext.
-
Known plaintext attack: Utilizing knowledge of a portion of the plaintext to determine the key or the remainder of the plaintext.
-
Differential and linear cryptanalysis: These methods involve analyzing the relationship between the input and output of a cryptographic system to determine the key or plaintext.
-
Side-channel attacks: Analyzing the connection between the input and output of a cryptographic system in order to derive its key or plaintext.
-
Algebraic attacks: These approaches derive the key or plaintext using mathematical aspects of the encryption process, such as the factorization of the modulus in a public key system.
What are the Types of Cryptanalysis?
There are several forms of cryptanalysis that are grouped into two basic categories: Classical and Modern.
-
Classical Cryptanalysis: Classical Cryptanalysis refers to the techniques used to attack encryption systems before the invention of computers. Classical cryptanalysis strategies are listed below:
- Frequency analysis
- Known plaintext attack
- Differential cryptanalysis
- Linear cryptanalysis
-
Modern Cryptanalysis: Modern Cryptanalysis refers to the techniques used to attack computer- and algorithm-based encryption schemes. Modern cryptanalysis strategies are given below:
- Brute force
- Side-channel attacks
- Algebraic attacks
- Differential and linear cryptanalysis
- Meet-in-the-middle attack
- Quantum Cryptanalysis
What are the Use Cases for Cryptanalysis?
Cryptoanalysis has the following applications.
-
Password Cracking: In order to recover forgotten or lost passwords, cryptanalysis software can conduct dictionary and brute-force attacks on password-protected systems.
-
Network Security: Cryptanalysis can be used to find and take advantage of network security flaws, like wireless network encryption flaws.
-
Penetration Testing: Cryptanalysis is a technique that can be used in penetration testing to find security flaws in encryption systems so that they can be fixed.
-
Vulnerability Assessments: Cryptanalysis can be used to carry out vulnerability analyses of encryption systems in order to spot and reduce security risks.
-
Malware Analysis: By decrypting the encryption used by malware to conceal its payload and commands, cryptanalysis can be used to analyze and understand the behavior of the threat.
-
Information Gathering: Intelligence agencies employ cryptanalysis to decrypt and extract data from enemy messages and communications.
-
Forensics: During digital forensics investigations, cryptanalysis can be used to decode and examine data, such as digital evidence in criminal cases.
-
Secure Communication: To prevent unwanted access to sensitive information, cryptanalysts can aid in the design and implementation of secure communication systems.
What are the Examples of Cryptanalysis?
There are several examples of cryptanalysis in the past and now. Here are some noteworthy examples:
-
World War II: The Allies were able to decipher the German Enigma machine and the Japanese Purple code, providing vital intelligence that contributed to their triumph. This was a significant accomplishment in the realm of cryptanalysis, and it proved the need for decryption during wartime.
-
RSA Encryption: RSA is one of the most used encryption methods, and it has been the focus of a number of cryptanalysis attacks. Using a technique known as the General Number Area Sieve, a team of researchers proved in 1991 that it was feasible to factorize a huge RSA key, marking a significant advancement in the field of cryptanalysis.
-
AES Encryption: The United States government has accepted the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) for use in sensitive communications. In 2009, a group of academics released a paper describing a new method for cracking AES encryption, demonstrating that AES was not entirely safe.
-
WPA/WPA2: WPA and WPA2 are wireless network encryption technologies. In 2017, a flaw in WPA2 known as KRACK (Key Reinstallation Attack) was identified, allowing attackers to capture and decode wireless network communications.
-
HTTPS Certificate: Researchers revealed in 2011 that a bogus certificate authority had issued a number of SSL certificates that might be exploited to eavesdrop on and decode encrypted conversations.
-
Quantum Computing: With the advent of quantum computing, the prospect of a new sort of cryptanalysis known as quantum cryptanalysis, which can break the majority of encryption techniques now in use, is becoming a reality.
What is the Role of Cryptanalysis in Cybersecurity?
The goal of cryptanalysis in cybersecurity is to find exploitable flaws and vulnerabilities in cryptographic systems. By breaking or uncovering the secret meaning of a cryptographic system or message, cryptanalysis can reveal significant insights into the system's security, which can subsequently be utilized to enhance the system's security or design defenses against attacks. Several sectors of cybersecurity make use of cryptanalysis, including:
-
Penetration Testing: By replicating a real-world attack and discovering weaknesses, cryptanalysis may be used to assess the security of encryption systems.
-
Incident Response: Encrypted data and conversations recorded during a security event may be analyzed using cryptanalysis to determine the nature of the attack and identify the attackers.
-
Digital Forensics: For judicial processes, cryptanalysis can be used to decrypt digital evidence.
-
Network Security: Cryptanalysis is utilized to detect and exploit vulnerabilities in network encryption technologies in order to acquire unauthorized network access.
-
Cyber Espionage: Governments and intelligence agencies employ cryptanalysis to access sensitive information and conversations.
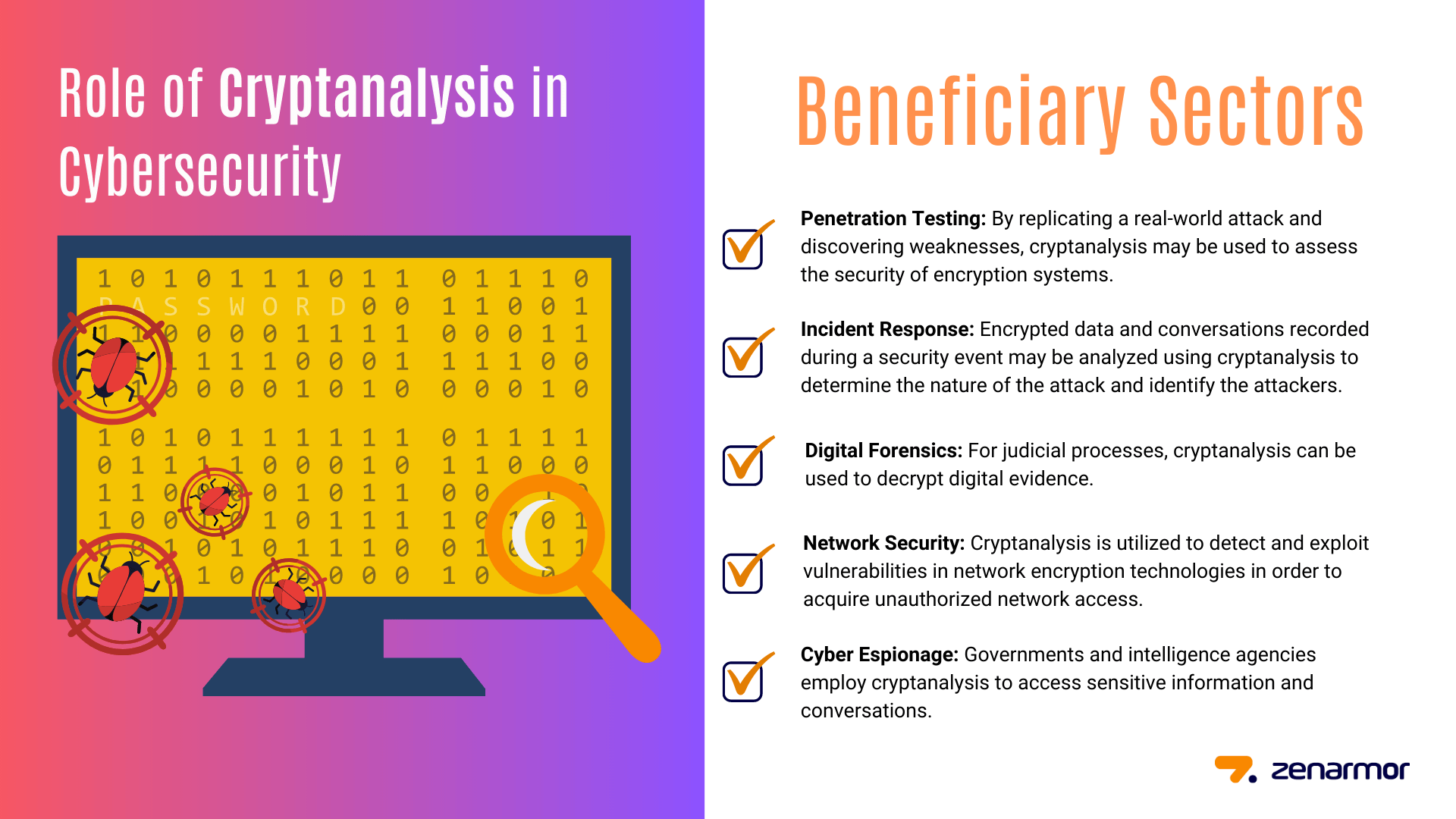
Figure 1. Cybersecurity sectors that use crytoanalysis
Is Cryptanalysis still Used?
Yes. Cryptanalysis is still utilized in the cybersecurity industry today. As encryption algorithms and cryptographic systems evolve, so too do the methods used to attack them. Cryptanalysis is essential for discovering flaws and vulnerabilities in cryptographic systems, and it continues to play a significant role in assessing the security of encryption systems, incident response, digital forensics, and other areas of cybersecurity.
Cryptanalysis is employed in the creation of new encryption algorithms and cryptographic systems. By exposing these new systems to rigorous cryptanalysis, researchers and engineers are able to uncover and address any possible flaws prior to the systems' deployment in the real world.
It is vital to highlight that the legality of cryptanalysis depends on the environment and the intended goal of the analysis.
How do you Learn Cryptanalysis?
Cryptanalysis is a difficult yet enjoyable subject to study. Here are several methods for learning cryptanalysis:
-
Learn the Basics of Cryptography: Before you can begin to study cryptanalysis, you must have a firm grasp of cryptography's fundamentals. This comprises encryption techniques, key management, and cryptographic protocols.
-
Study Mathematical Concepts: Numerous mathematical ideas, such as number theory, probability, and abstract algebra, are frequently utilized in cryptanalysis. By studying these ideas, you will be able to comprehend the mathematical basis of encryption methods and how they might be attacked.
-
Read Books and Articles on Cryptanalysis: Numerous books and articles on cryptanalysis give an in-depth examination of the various approaches and methods employed in the discipline. The books "Introduction to Cryptography" by Johannes Buchmann, "Cryptanalysis of Number-Theoretic Ciphers" by Andreas Enge, and "The Code Book" by Simon Singh are highly recommended.
-
Take Online Courses: Several online courses give an introduction to cryptanalysis, such as the Massachusetts Institute of Technology's "Cryptanalysis and Information Security" course.
-
Practice: Practice is the greatest method to learn cryptanalysis. You can attempt to crack simple encryption algorithms and ciphers, or you can take part in capture-the-flag (CTF) events, which are online tournaments where you can pit your talents against those of other competitors.
-
Join Online Communities: Joining online forums of cybersecurity aficionados, such as Reddit or LinkedIn groups, can help you interact with others interested in cryptanalysis and exchange information and tools.
Cryptanalysis is a complicated area that involves knowledge of cryptography, mathematics, and computer science; therefore, learning it demands time and effort. However, with perseverance and hard work, you acquire the necessary skills and information to become successful in cryptanalysis.
What is the Purpose of Cryptanalysis Software?
The objective of cryptanalysis software is to facilitate the decryption and recovery of secret information. Software for cryptanalysis is used to undertake a variety of attacks against encryption algorithms and ciphers, including dictionary attacks, brute-force attacks, and other forms of cryptanalysis. Among the specialized uses for cryptanalysis software are:
-
Attempting to recover lost or forgotten encryption keys
-
Attempting to decrypt encrypted messages without the proper key
-
Attempting to find weaknesses in encryption algorithms that can be exploited
-
Attempting to crack password-protected files or systems
-
Attempting to identify and exploit vulnerabilities in network security
-
Attempting to analyze and understand the behavior of encryption algorithms and ciphers
The use of cryptanalysis tools for lawful reasons, such as penetration testing and vulnerability assessments, can assist detect and address security problems in encryption systems.
Remember that the usage of cryptanalysis software can be criminal if it is used to obtain unauthorized access to systems or data and that it should only be used by authorized persons within the law.
What are the Best Cryptanalysis Software Programs?
There are several cryptanalysis software tools, and the optimal one for a particular task depends on the encryption technique and message type being studied. Popular cryptanalysis software applications include:
-
John the Ripper: A free and open-source password cracking program that can execute dictionary and brute-force attacks on a variety of encryption methods, including Unix passwords and Windows LM hashes.
-
Cain and Abel: A program that can execute a range of cryptanalytic attacks, such as network sniffing, decrypting encrypted passwords, and disclosing password boxes.
-
Hashcat: An open-source password cracking program capable of a variety of hash attacks, including dictionary, brute-force, and combinator attacks.
-
Cryptool: Free and open-source software that is used for a variety of cryptographic activities, such as encryption, decryption, and cryptanalysis.
-
Aircrack-ng: Aircrack-ng is a set of WiFi network security evaluation tools. It concentrates on many aspects of WiFi security.
Who Uses Cryptanalysis?
The following organizations or groups use cryptanalysis:
-
Governments: Governments and intelligence agencies use cryptanalysis to gain access to sensitive information and communications. Using cryptanalysis, governments and spy services get access to sensitive information and conversations. Cryptanalysis is utilized by military groups to acquire a tactical edge in combat.
-
Cybersecurity Teams: Professionals in cybersecurity employ cryptanalysis to detect and exploit vulnerabilities in encryption systems in order to safeguard businesses from cyberattacks.
-
Hacker and Researchers: White hat hackers and security researchers employ cryptanalysis to assess the security of encryption systems and identify exploitable weaknesses.
-
Criminal Groups: For financial or political advantage, criminal groups and nation-state players utilize cryptanalysis to obtain illegal access to sensitive information.
Who are Cryptanalysts, and What are Their Roles?
Cryptanalysts are experts who specialize in the study of techniques for deciphering encrypted data without having access to the secret information ordinarily necessary to do it. They examine and crack encryption schemes and ciphers using their expertise in mathematics, computer science, and languages. They play a crucial role in the realm of information security by identifying and exploiting vulnerabilities in encryption schemes. Among the primary responsibilities of a cryptanalyst are as follows:
-
Analyzing encryption methods and ciphers to uncover exploitable holes and vulnerabilities
-
Developing strategies and procedures for decrypting and retrieving concealed data
-
Conducting pen testing and vulnerability assessments to discover and mitigate security threats.
-
Implementing and designing safe encryption systems
-
Advising corporations and government agencies on encryption and information security best practices
-
Working with other information security experts to create and execute security methods
-
Keeping abreast of the most recent research and advancements in cryptography and cryptanalysis
Government agencies, such as the National Security Agency, and commercial organizations in the field of information security employ cryptanalysts. They also operate as independent researchers or consultants.
What is the History of Cryptanalysis?
Cryptanalysis, the study of techniques for deciphering encrypted information without access to the secret information, dates back thousands of years. Ancient civilizations such as the Egyptians and the Greeks employed rudimentary substitution ciphers to encrypt communications, providing some of the oldest known examples of cryptanalysis.
Cryptanalysis had a major part in determining the result of World War II. The Allies were able to decipher the German Enigma machine and the Japanese Purple code, providing vital intelligence that contributed to their triumph. This resulted in the development of several new encryption schemes and computers to aid in the process of decoding.
With the emergence of new technology and the growing use of encrypted electronic communications, the discipline of cryptanalysis has continued to expand in the contemporary day. With the emergence of the Internet, cryptanalysis has become a crucial technique for securing sensitive data, such as financial transactions and personal information.
The development of computer technology has had a substantial impact on the subject of cryptanalysis. Computer algorithms capable of doing difficult mathematical calculations and analyzing massive quantities of data have been devised, making it feasible to break encryptions that would have been impossible to crack using conventional methods.
Overall, the history of cryptanalysis has been characterized by a perpetual struggle between those who design encryption systems and those who attempt to break them. As encryption technology evolves, cryptanalysis continues to play a vital role in protecting sensitive data.