Cybersecurity Analytics: Importance and Benefits
Cybersecurity analytics is the application of sophisticated analytics to detect, monitor, and safeguard the digital environment of an organization.
Organizations struggle more than ever to defend themselves against cyberattacks due to the sophistication of their opponents and the need to achieve more with fewer resources.
Organizations can no longer depend only on traditional software-based protection solutions and approaches because they cannot keep up with rapidly evolving threats.
They require improved methods to comprehend what is occurring within their networks, endpoints, and other systems.
The new approach uses big data technologies along with a variety of data sources (event logs, network packets, user behavior) to create insights that can be used to generate pertinent alerts that can then be manually investigated or have automated responses taken, depending on the severity of the alert.
We will explore the many facets of cybersecurity analytics in this article, including their advantages, significance, application domains, tools, and platforms, as well as the similarities and differences between them and other concepts.
What is Cybersecurity Analytics?
Cybersecurity Analytics is the process of accumulating data for the purposes of collecting evidence, constructing timelines, and assessing capabilities in order to conduct and develop a proactive cybersecurity strategy that detects, analyzes, and mitigates cyber threats.
With a conventional security information and event management (SIEM) system, you must rely on evaluating network conditions at a single point in time. Cybersecurity analytics applies to the whole network, taking into account general patterns that may not be apparent in a specific snapshot.
What are the Benefits of Cybersecurity Analytics?
There are many advantages to security analytics that conventional security does not offer. One of the main advantages of security analytics is the ability to quickly analyze diverse sets of enormous data. Cybersecurity analytics consists of the following data:
-
Network traffic
-
Cloud use and traffic
-
Business applications
-
Endpoint and user behavior data
-
Non-IT contextual data
-
External threat intelligence
-
Access and identity management data
-
Proof of compliance during an audit
Organizations are given a thorough understanding of events through the analysis of these various data sources. Analytics provides proactive security incident detection and quicker response times that assist the company in preserving the integrity of systems and data by tying together these data sources. The following highlights the main advantages that analytics have for organizational security.
-
Proactive Security: Security analytics used for proactive security quickly finds signs of any suspicious activity by comparing events with logging data and other sources in close to real-time. This serves as the cornerstone of a proactive security posture that enables businesses to identify threats earlier and respond to them more quickly.
-
Maintaining Regulatory Compliance: Security analytics can be used to follow industry and governmental regulations like PCI-DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR. The analytics keeps track of user behavior, access, and authentication to enable the detection of insider threats and record data for auditing. Security analytics additionally provide reporting capabilities with a unified view of all data events that pinpoint potential non-compliance.
-
Improved Incident Forensics: Tools for data analytics provide details about the location of an attack, what happened, and the type of damage or exploit that was used. Each of these is vital for digital forensics. Security teams can create an accurate attack timeline and avoid repeat incidents in the future thanks to these attack insights.
For threat analysis, advanced data analytics uses machine learning and statistical models to detect abnormalities in real time. These capabilities combine precise security warnings with extra forensic data in order to detect and respond to cyber-attacks. Advanced analytics decrease the effort of security teams by automatically initiating procedures when insider threats or other dangerous behaviors are discovered.
What is a Cybersecurity Analytics Solution?
Security analytics solutions identify and diagnose risks using both real-time and historical data. Examples of information sources:
-
Workstations, servers, sensors, mobile devices, and other endpoints can provide warnings in real time.
-
Streaming data from other IT security apps (firewalls, intrusion prevention, endpoint detection and response, etc.).
-
Network traffic volume and types.
-
Server logs.
-
Third-party cyber threat intelligence feeds.
Security analytics collects data from several sources and searches for abnormalities and connections within the data.
A security analytics tool employs a variety of data analysis techniques. Among these are conventional rule-based approaches, statistical analysis, and machine learning. Additionally, the application integrates additional components to automate and choreograph events.
The key components of a security analytics system are outlined below:
-
Behavioral Analytics: Typically, abnormal user or application activity implies a security breach or assault. Behavioral analytics identifies abnormalities by analyzing patterns of the user, application, and device activity. Financial services organizations, for instance, use behavioral analysis to detect credit card fraud. An abnormally large transaction (or a $1 test withdrawal) may indicate that a card number has been compromised. Similarly, an end-user who goes in at 2:00 a.m. to access non-work-related systems or an application that begins sending strange requests and commands might suggest a security compromise.
-
Network Analysis and Visibility (NAV): A NAV application or device analyzes network traffic generated by end users and apps. Forrester Wave's research on Security Analytics Platforms defines NAV as a collection of technologies including network discovery, flow data analysis, network metadata analysis, packet capture, and analysis, and network forensics.
-
Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR): SOAR is the orchestration hub that coordinates communication between data collection, the analytical engine, and threat response applications. SOAR features are provided by either the security analytics application or an external product, such as a security information and event management (SIEM) program. A SIEM gathers information on network traffic, system events, and possible threats. The system then does analytical operations, including correlation and statistical analysis.
-
Forensics: Security data analytics solutions offer instruments for investigating previous or current attacks, determining how IT systems were infiltrated, and identifying lingering vulnerabilities. This aids in preventing future events of a similar nature.
-
External Threat Intelligence: Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) is not security analytics in and of itself. Nevertheless, CTI platforms (TIPs) provide context to an analytical procedure. A provider of security software and services incorporate a cyber threat intelligence (CTI) feed into its solution. Examples of intelligence feeds include the Department of Homeland Security's free Automated Indicator Sharing (AIS) and the Swiss security website Ransomware Tracker, which focuses on tracking and monitoring the status of ransomware-related domain names, IP addresses, and URLs. These elements support a security analytics program's ability to identify and stop advanced persistent threats and complex attacks (APT). APTs are carried out in phases, each of which may appear harmless, but which, when combined, can result in a security vulnerability.
What is the Importance of Automation in Cybersecurity Analytics?
Cybersecurity analytics technology and automation is a field of cybersecurity that offers an automated way to discover, prioritize, and resolve security issues, all with the aim of maintaining continuous, real-time monitoring of your network environment. With big data systems to manage enormous quantities of streams from numerous devices and apps in a single area, you can monitor suspicious activities with minimal manual analysis.
Security professionals now have access to machine learning tools that enable them to evaluate multidimensional datasets in milliseconds using clever algorithms that reveal hidden links between varied sorts of events (e.g. endpoint/user behaviour).
These sophisticated approaches enable enterprises to detect malicious activity swiftly, enabling them to respond faster than ever before by automatically blocking threats or delivering alarms to on-duty security experts.
Why is Machine Learning Necessary in Cybersecurity Analytics?
The definition of machine learning is "a form of artificial intelligence (AI) that enables systems to automatically learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed".
Machine learning's uses vary from computer vision to sophisticated robotics systems. Machine learning has made its way into cyberspace. For instance, hackers attempt various web vulnerabilities such as SQL injection and LFI (Local File Inclusion). Hackers are growing more sophisticated, and automated vulnerability scanners are frequently used to discover new flaws. We cannot keep up with the rate at which hackers advance, but we can learn quicker than them using machine learning.
What are the Different Types of Security Analytics Tools?
Numerous cybersecurity data analytics technologies provide businesses with a variety of features that may be combined and enable improved threat detection and prioritization. Using behavioral analysis, they direct and develop reaction methods. In addition, they are accessible as hardware, software, or cloud-based virtual solutions.
Common cybersecurity analytics technologies that provide some of the aforementioned advantages are as follows:
-
Behavioral Analytics Tools: Behavioral analytics technologies are tasked with evaluating the behavior of users, apps, and devices on the network and looking for patterns and trends that may signal a security breach.
-
SIEM Tools: Security information and event management (SIEM) is a collection of technologies that analyze network device alarms in real time.
-
SOAR Tools: SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) is a single hub that connects data collection, analysis, and threat response capabilities.
-
NAV Tools: Multiple tools are utilized by network analysis and visibility (NAV) to examine end-user and application traffic. NAV monitors this data in real-time as it traverses the network.
-
Forensic Tools: Forensic tools are utilized to analyze current and historical assaults in order to determine how attackers have infiltrated security systems and weaknesses.
-
External Threat Intelligence Tools: External threat intelligence technologies are often bundled as a portfolio of analytical methods that may enable cybersecurity data analytics and are typically provided by external organizations.
What are the Benefits of Cybersecurity Analytics Tools?
The primary advantages of cybersecurity analytics tools are explained below:
-
Automated Threat Intelligence: In some respects, cybersecurity analytics resembles the next-generation SIEM, especially in how it automates threat intelligence. With ML technologies, risks are identified, classified, and stored for future use in detecting similar threats.
-
Prioritized Alerts: With cybersecurity analytics, you prioritize the most important alerts even if a large number of cyber threats causes your system to be bombarded with notifications. This frees up additional time for your IT staff by decreasing the time spent investigating erroneous or less-than-critical alarms.
-
Proactive Incident Detection: A reactive approach to cybersecurity leaves your system vulnerable to emerging or innovative attacks. Cybersecurity gives you a proactive method to detect and mitigate risks, providing you with a global perspective of not just what your network is now dealing with, but also potential future threat occurrences. This gives a comprehensive profile of the intelligence threats that your network confronts.
-
Improved Forensic Incident Investigation: With security analytics, you determine where attacks originate, how they entered your system, and which assets they compromised. A timeline of the events that happened can also be established for subsequent examination.
Which Issues are Resolved by Cybersecurity Analytics Tools?
When incorporated into a complete cybersecurity program, cybersecurity data analytics technologies aid security professionals in resolving several issues. This includes increased detection and reaction times, enhanced cyber threat hunting, detection of insider threats, identification of illegal access, cloud security monitoring, and analysis of network traffic.
In addition, cybersecurity analytics technologies may assist in resolving issues as diverse as
-
Integration Problems: Cybersecurity analytics technologies enhance the integration of pertinent data from a wide variety of sources.
-
Visibility Issues: Tools that enhance the visibility of network security analytics assist in addressing fast-changing threats on extremely complex IT infrastructures and in monitoring internal networks more effectively.
-
Detection and Forensic Difficulties: Cybersecurity analytics technologies aid in the resolution of detection and forensic issues by automatically aggregating additional data.
-
Prioritization Problems: As real-time analytical tools, cybersecurity analytics resolves prioritization problems by elevating the most urgent risks and enabling security teams to address them immediately.
-
Compliance Difficulties: Adaptable and versatile, cybersecurity analytics technologies resolve compliance issues by enhancing insight into HIPAA and PCI-DSS, as well as by fast adapting to regulation change.
Security Analytics with Zenarmor
When the firewall data, which is one of the most significant sources of cyber security analytics, is analyzed, you acquire comprehensive information on the cyber security state of your organization.
Zenarmor, which is utilized as an NGFW extension in open-source firewalls provides you with extensive security analytics information.
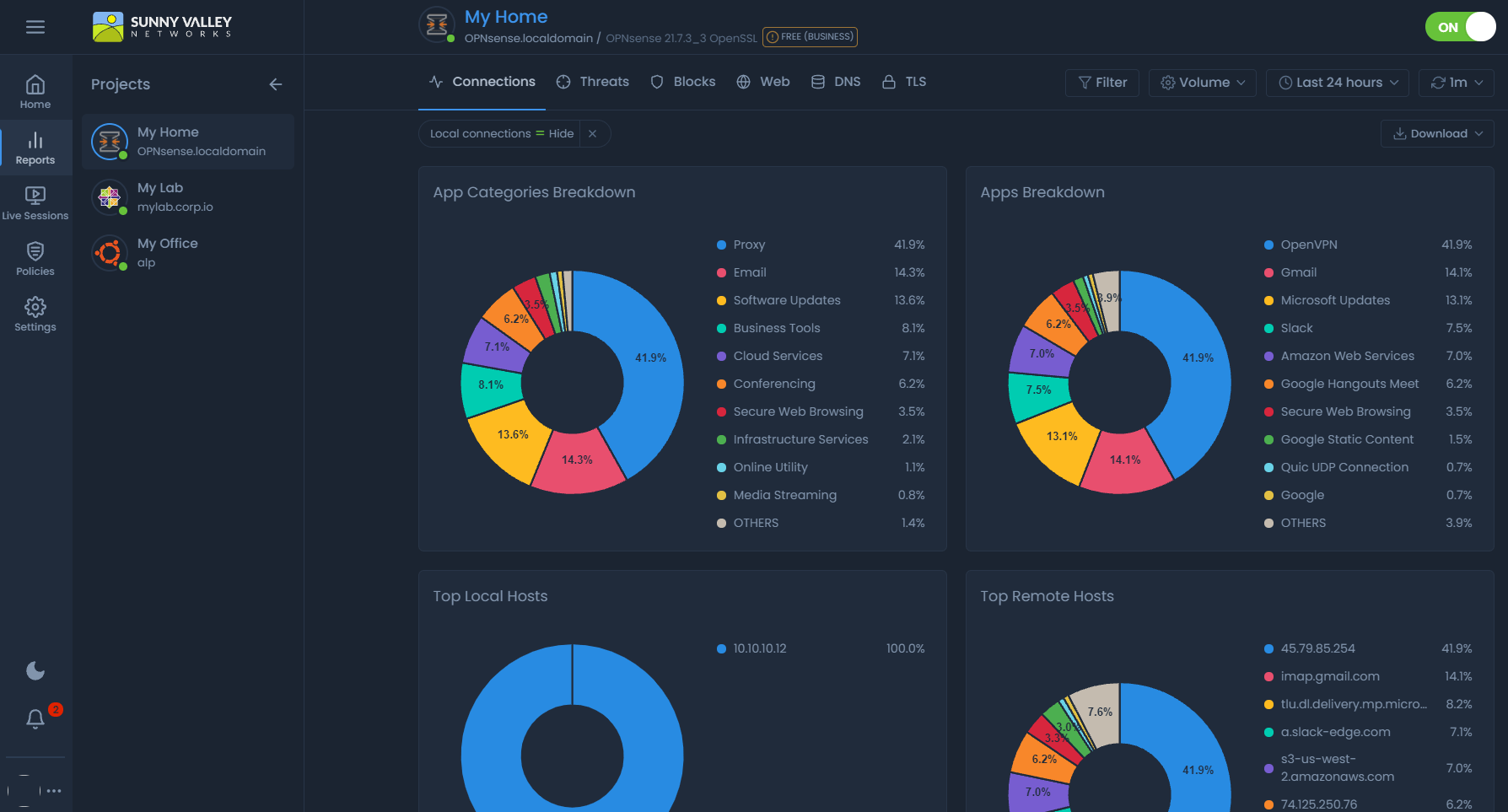
Figure 1. Advanced Analytics on Zenarmor
In the cyber security sector, Zenarmor provides the most sophisticated reporting and analytics. Zenarmor provides extensive report views that enable you to study both the overall picture and the per-connection details. The reports may be filtered to only show the desired data.
Your network's traffic statistics and threat activity sessions may be examined at various time periods. With the reporting features of Zenarmor, you can instantly discover network security risks throughout your whole network (s).
What is the Difference Between SIEM and Cybersecurity Analytics?
Cyber Security Analytics originated from Security Incident and Event Management (SIEM) to fulfill the requirement for enhanced business-wide security; more context and insights. Security Incident and Event Management (SIEM), Behaviour Anomaly Detection (BAD or UEBA), and Threat Intelligence are the three important components.
SIEM mainly relies on point-in-time testing, which leaves room for mistakes in the continuously changing data entering and exiting the network. This implies that it cannot handle continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) like cybersecurity analytics real-time technologies. SIEM has applications within businesses, but cybersecurity analytics used in conjunction with SIEM may gather log data from network devices and data from real-time events and code modifications.
What are the Differences Between Data Analytics and Cybersecurity Analytics?
It may be claimed that the discipline of cyber analytics is the product of a marriage between data analytics and cybersecurity. To acquire a clear understanding of where cyber analytics, also known as security analytics, fits between these bookends, we must first explore the definitions of these three fields of study.
The act of analyzing datasets to derive conclusions about the information they contain is known as data analytics. The discovery and examination of data patterns can yield valuable insights. For creative data utilization, scientists categorize data as descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, or prescriptive. It aids businesses in gaining a deeper understanding of client purchasing patterns, measuring the effectiveness of advertising campaigns, identifying new markets, and developing new goods.
Cybersecurity is the activity of safeguarding digital assets against hostile assaults. It is the other parent of cyber analytics or security analytics. This field utilizes a variety of approaches, tactics, procedures, and instruments to diagnose, anticipate, and prevent unwanted access to networks, systems, and devices.
Cyber analytics, often known as security analytics, is the application of data analytics to achieve a cybersecurity goal. It is a strong data-driven tool that can define cybersecurity threats, identify vulnerabilities, forecast future hostile activity, and prescribe defensive measures.
Cyber analytics has established the foundation for key cybersecurity solutions and practices during the past few decades. It has offered significant insight into the strategies and habits of evil actors.
What is the History of Cyber Analytics?
There has always been a dance between attackers and defenders in cybersecurity. Initially, defenders utilized primitive signatures such as file hashes and IP addresses to identify fraudulent activity. However, once attackers gained knowledge of these security restrictions, they modified their techniques to circumvent recognized signatures in order to evade detection.
In response, defenders implemented more adaptable approaches, such as deep packet inspection and the identification of binary sequences within files. Simultaneously, cybersecurity controls began employing more heuristics for detection and mitigation, providing defenders with a more accurate understanding of whether detected behavior was hostile.
Cyber analytics utilize the detection of anomalies and other statistical approaches to find variations from prior behavior. Innovative and potent technologies, such as machine learning and deep learning, enhance detection and mitigation capabilities. These strategies make it possible to address a much larger range of bad activities and are more difficult for attackers to circumvent. Advanced Network Detection and Response systems utilize cyber analytics to detect cyber threats to networks depending on the behavior of the threat.