What is Network Detection and Response (NDR)?
Networks are expanding into the cloud and growing in size and complexity regularly. This has resulted in an unprecedented amount of data crossing the distributed network, creating the ideal setting for hostile actors to hide. The network is the most convenient means of initiating cyberattacks, and cyber threat actors are constantly evolving techniques that circumvent enterprise network security solutions. These novel risks necessitate advanced network security solutions, such as Network Detection and Response (NDR), to prevent and detect them.
NDR is a new type of cybersecurity solution designed to safeguard the complex requirements of on-premises, public and private clouds, and hybrid environments in the most efficient manner feasible.
Network Detection and Response (NDR) solutions continuously monitor your corporate network by collecting all network traffic for unprecedented visibility and using behavioral analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence to detect cyber threats and anomalous behavior, and respond to these threats by integrating with other cybersecurity solutions.
NDR systems enable businesses to identify traffic anomalies that signal command and control, lateral movement, exfiltration, and malware activities. To correctly identify cyberattacks, they examine north-south traffic between internal hosts and the internet, as well as east-west traffic between internal hosts, including internal servers.
When NDR is integrated with other security solutions, such as log analysis tools (SIEM) and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), network blind spots can be closed and a more robust cybersecurity strategy can be developed. NDR solutions offer more comprehensive data than EDR tools, which are limited to endpoints. They also provide more detailed data than SIEMs, which rely on log data that can be manipulated by attackers and is not as granular as the network packet data utilized by NDR systems.
NDR systems enhance security capabilities by automating responses to threats, which enables security and network operations teams to communicate more efficiently, resulting in improved detection and mitigation. Additionally, NDR solutions lessen the strain on security resources, allowing workers to focus on other crucial responsibilities.
In this article, we will cover what Network Detection and Response (NDR) is, how it works, why organizations need NDR solutions, and what benefits they get when implementing an NDR solution on their IT infrastructure. In addition, you will learn what EDR and XDR are and how NDR differs from them.
What Does NDR mean?
Network Detection and Response (NDR) is a cybersecurity solution that oversees the entire organization's network to identify cyber threats and anomalous behavior using non-signature-based tools or techniques and react to these threats using either native capabilities or by integrating with other cybersecurity tools. In the early 2010s, network detection and response (NDR) technologies evolved to identify and halt evasive network threats that could not be easily blocked using established attack patterns or fingerprints.
Network detection and response (NDR) systems detect abnormal network activity using a combination of non-signature-based advanced analytical approaches, such as machine learning, artificial intelligence. This helps teams respond to attacks and traffic anomalies missed by traditional security technologies.

Figure 1. What is NDR?
Why Do You Need NDR?
People often think that Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions are enough to protect enterprise networks. Although these tools help IT security teams get started, networks have become a more valuable target for smart attackers because IoT devices, cloud computing, and digital transformation have become more popular. This makes NDR solutions an essential part of the SOC Visibility Triad for finding threats. Network Detection and Response (NDR) is crucial to the security of IT infrastructure.
Gartner recommends that security teams use all three types of cybersecurity solutions (SIEM, EDR and NDR) to make a Security Operations Center (SOC) Visibility Triad. This is a proactive way to reduce the chances of a threat actor staying on a private network long enough to get what they want.
To protect a company from cyber threats, comprehensive network visibility and advanced threat prevention and detection capabilities are required. Traditional, signature-based detection techniques are frequently unsuccessful against contemporary threats, giving organizations a false sense of security. NDR security solutions give enterprises an additional layer of threat prevention and network-level security capabilities.
A security solution that focuses on detection seeks to identify a potential danger and then relies on a security analyst to undertake an incident response based on a generated alert. This means that incident response occurs only after the attack is effective, and rapid and automated cyberattacks may have already accomplished their goal before an alarm is detected, and a response is initiated. An NDR security system includes automated response capabilities that allow it to prevent an attack before any damage is done, as opposed to responding after the fact.
Signature-based detection algorithms employed by numerous legacy security solutions, such as classic antivirus and intrusion detection systems, (IDS), are ineffective in detecting contemporary threats. Malware used by cybercriminals is frequently designed to vary from campaign to campaign, rendering signatures obsolete as soon as they are generated. A NDR solution employs sophisticated detection capabilities based on machine learning and data analytics to identify and respond to novel cyber threats for which signatures have not yet been developed.
Modern IT environments are getting the attack surface bigger and make cyber defense even more difficult. With the rise of cloud applications and "bring your own device" (BYOD) policies, which made it possible for mobile devices, third-party services, and IoT devices to be everywhere, the traditional idea of a network perimeter died. IoT devices are especially troublesome because updates from the manufacturer can be slow, and endpoint security is hard to set up. As 5G networks come online, the IoT security problem is going to get a lot worse. This is because 5G will bring a new era of enterprise IoT devices with new risks and vulnerabilities, as well as a lot more traffic to monitor and secure.
NDR is a great solution if your team works in an environment with Internet of Things (IoT), operational technology (OT), or industrial control systems (ICS) devices, you can't install agents for endpoint-based detection. For example, organizations with Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems can use NDR to monitor and inspect traffic flow between devices and send alerts about protocols that are rarely seen.
Digital transformation projects that include cloud, mobile, and IoT are making it harder for security teams to see suspicious traffic and are also making it easier for hackers to get into a private network. Security in the cloud is especially hard because mistakes can happen without being noticed, and cloud forensics is hard in its own way. Gartner says that until 2025, the customer will be to blame for 99 percent of cloud security failures.
"Encryption everywhere" is a push that adds to the problem. Different sources say that most traffic today is encrypted, which makes it hard to look at that traffic. Attackers can hide their own bad behavior in encrypted traffic to get past the network's perimeter or move laterally inside the network. 91 percent of organizations are worried that they will lose security visibility because of encryption and the use of the cloud.
Another problem is that remote working has raised the need for remote network access and, thus, the danger to company networks. The personal computers and mobile devices that workers use to access the internal network may not have been subjected to rigorous malware-scanning procedures. The usage of VPNs and proxy avoidance apps by workers, which may circumvent a company's lax remote access restrictions, exacerbates the problem. By infecting a remote user's device with malware, such as via a phishing attempt, attackers may quickly enter a company's network.
NDR is a good option for security teams that want to see what's going on in on-premise, remote, and cloud environments with a single solution. NDR is the best way for your team to see everything on your network and not have to worry about what it can't see.
By providing real-time network visibility, an NDR solution enables the detection of concealed harmful activity such as APT, ransomware, and complex supply chain assaults, such as SUNBURST. Suppose opponents were able to penetrate your defenses and get access to your network through third-party apps. In this instance, they will not have sufficient time to begin their lateral movement and infection of other network locations, since the NDR solution would identify them and instantly alert the security staff.
How Does NDR Work?
According to the 2020 Gartner Market Guide for Network Detection and Response, NDR solutions use non-signature-based methodologies, such as machine learning or other analytical techniques, to detect suspicious activity on enterprise networks. NDR tools continually analyze raw traffic and/or flow records, such as Net Flow, in order to construct models that reflect typical network activity. When NDR tools identify abnormal traffic patterns, alarms are generated. Response is another crucial component of NDR solutions.
Unlike many log management and security analytics packages that emphasize security alerts, NDR systems analyze raw network traffic records to identify dangers. While they can also be deployed as a passive network element that collects data via network switch SPAN ports or physical TAPs, a growing number of NDR systems can also collect network traffic data from existing network infrastructure, such as network firewalls, making deployment easier.
High-performance Network Detection and Response (NDR) solutions employ powerful machine learning and artificial intelligence methods to model adversary tactics, techniques, and procedures that are documented in the MITRE ATT&CK architecture in order to precisely detect the attacker's actions. They expose security-relevant information, extract high-fidelity data, and correlate events across time, users, and apps to substantially reduce investigative time and effort. In addition, they transmit security detections and threat correlations to security information and event management (SIEM) solutions for comprehensive security evaluations.
NDR systems go beyond only detecting threats; they respond to threats in real-time through native controls, or provide a vast array of integrations with other cybersecurity tools or solutions such as security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR).
Some tools and methods that are often used by NDR solutions are as follows:
-
Signatures: Signature-based detection methods use a unique identifier called an indicator of compromise (IOC) to find a known threat in the future. Signatures used to work well, but in a world where custom malware, malware toolkits, and non-malware-based attacks like credential replay are common, the process of using unique identifiers to protect against known threats is becoming less and less useful. Nearly 75% of all network traffic today is encrypted. This is part of a growing trend that makes signature-based tools useless because they can't look at the content, which is needed to match certain types of IOCs. NDR systems go beyond signature-based detection to examine network traffic with machine learning and data analytics. This allows them to recognize patterns and identify anomalies in network data, enabling the detection of malicious or suspicious traffic.
-
Threats Intelligence Feeds: Threat intelligence feeds are streams of data that have information about cyber threats that have already been found. Network detection and response systems utilize threat intelligence from both inside and outside the company. If threat intelligence is up-to-date and usable, it can help NDR solutions find known threats or give more information about a detected network anomaly so that it can be ranked by risk. The main function of an NDR solution is to offer SOC analysts information about their network's current security posture and threats. The NDR generates a stream of security alerts highlighting potentially harmful and suspicious network traffic.
-
Statistical Analysis: Statistical analysis is a good way to understand how people act, and a few NDR providers sometimes market it as "AI". These can range from simple outlier analysis (e.g., which URL hasn't been seen in this group of devices) to basic Bayesian analysis of network traffic patterns to other statistical methods. Usually, a sample is used to find a baseline, which is then used to figure out which activity is different from normal network traffic. This lets SOCs model normal network traffic and point out suspicious traffic that falls outside the normal range. NDR security systems scan network traffic and extract patterns that may indicate abnormal or suspect connections. This information is used by the NDR solution to generate automated responses and is sent to Security Operations Center (SOC) analysts to aid in their incident investigation efforts.
-
Machine Learning: Machine learning uses the power of computers to look at a lot of data and make more accurate predictions. With NDR solutions, machine learning models can use behavioral analytics to find "unknown" threats to your network. Algorithms that use machine learning can see cyber threats coming (like ports being used for the first time that have never been used before), which speeds up triage and fixes. Machine learning models are also used to re-prioritize possible threats based on what is happening in the real world.
-
Heuristics: Heuristic analysis finds threats by looking at data for things that seem odd. In NDR solutions, heuristics make signature-based detection methods more powerful by allowing them to look beyond known threats and find suspicious traits in unknown threats and changed versions of known threats. Some companies that sell network sandboxes see file-based malware analysis as a type of network behavioral analysis.
-
Threat Protection: In addition to notifying security analysts of potential dangers, NDR solutions can also act automatically and proactively to thwart cyber attacks. Threat protection involves employing firewalls and other security measures to prevent suspicious or known-bad traffic from reaching its intended destination, disrupting the attack.
What are the Benefits of Network Detection and Response?
Network Detection and Response (NDR) tools and solutions offer the following benefits:
-
Improved Visibility: Network Detection and Response (NDR) tools monitor all traffic flows, whether entering and exiting the network or moving inside the network, so that teams have the extended network visibility required to identify and mitigate security issues regardless of the source of the threat.
NDR systems literally observe each and every network event an attacker generates. Unless the attacker acquires direct access to the one site containing the targeted, important, or sensitive data, he/she must undertake hundreds of network operations in order to achieve the desired end result. NDR solutions are capable of detecting all of these events, even the early network-based command and control and discovery operations that will seldom, if ever, generate a log event. In addition, NDR products are used in the later phases of an attack, such as lateral movement and exfiltration.
Enterprises frequently miss internal recon or discovery efforts, which can be the longest and most iterative stage of an active attack, if they don't monitor network traffic. They will hardly ever come across network activity like port scans, network scans, command and control communications, or other network-based attack techniques.
-
Fast Threat Response: NDR attributes malicious behavior to a particular IP address and conducts forensic analysis to determine how attacks have spread laterally throughout an environment. This enables teams to determine what other devices may be infected, resulting in quicker incident response, threat containment, and protection against negative business repercussions.
-
Streamlined Security Operations Center (SOC) Operations: AI-driven NDR solutions are automated and significantly improve security detections and security operations center (SOC) operational efficiency by providing full attack reconstructions and information needed to act on alerts quickly and thoroughly.
-
Cloud-based Analytics: Today's network detection and response technologies are cloud-delivered. With this cloud-native strategy, teams no longer have to build new log servers on-premises to collect and analyze network data. Furthermore, modern NDR platforms can collect network logs from current network security products like network firewalls, removing the need for dedicated network sensors. NDR systems provide comprehensive visibility and threat detection with low overhead.
-
Improved Accuracy: NDR systems offer comprehensive context to view all network activities an attacker performs, which can enhance the accuracy of attack detection. They can see all aspects of an attacker's tactics and techniques, including network reconnaissance activities, user credentials used for lateral movement, administrative behaviors, access to rare file shares, command and control sites, and potentially the endpoint process responsible for the network event. By triangulating the attacker from many attack perspectives, NDR products can provide significantly greater assurance that an assault is in progress. This validation eliminates the false positives that affect the majority of security products. For instance, a user credential discovered as having anomalous access to a file share or internet domain that is rarely accessed can also be associated to a host device engaging in uncommon port scanning or internet communications. By evaluating various variables of behavior and comparing current behavior to a baseline, detection accuracy can be improved.
-
Advanced Detection Technology: Network Detection and Response (NDR) systems apply non-signature-based detection approaches such as behavioral analytics and machine learning to detect atypical network activity that is missed by conventional technologies.
-
Real-time Analysis: Network Detection and Response (NDR) solutions analyze raw network telemetry in real-time or near real-time and offer alerts in a timely manner to enable teams to reduce incident reaction times.
-
Time and Cost Savings: Network Detection and Response (NDR) provide response capabilities that can increase human incident response and threat hunting efforts or automate operations to save teams time. Moreover, the NDR system saves money with a single, powerful detection and response tool that works in on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments
-
Network Behavior Analysis: Network Detection and Response (NDR) tools create a baseline of what regular network behavior entails and notify security teams of any unusual network traffic that goes outside this range.
-
Compliance: NDR solutions are useful to close compliance gaps.
What Types of Cyberattacks Does NDR detect?
The four most prevalent types of cybersecurity threats identified by NDR solutions are:
-
Insider Attacks: Employees or contractors engage in a variety of actions, such as accessing, stealing, and modifying files and data, altering access permissions, and installing malware.
-
External Attacks: External attackers who utilize social engineering, exploits, brute force attacks, or other techniques to breach applications or endpoints, acquire legitimate user credentials, establish command and control, move laterally, and steal, modify, or destroy data.
-
Risky Activities: Employees that are well-intentioned yet careless can expose their firms to assault. Sharing user accounts, exposing sensitive data to unauthorized people, and giving remote access to endpoints are examples of risky behavior.
-
Unknown Malware: External attackers who use undetectable malware to infect and take control of network hosts.
What are the NDR tools?
Choosing the correct NDR solution for your organization and budget might be difficult due to the range of options available. To choose an effective network detection and response solution for your organization, you must take a number of variables into account. First, you must choose if supervised or unsupervised machine learning would benefit you best. You must also choose if a managed, operated, or automated NDR system would suit you best. Other important considerations to consider include:
-
What does the overall ownership cost?
-
Which response technique, human or automated, best meets your security objectives?
-
To what degree is vendor support accessible in your region?
-
Is the NDR system's AI function entirely or partly reliant on rules?
-
What are the false-positive and false-negative detection rates?
-
Does the solution provide automated alert-to-action processes?
Some of the NDR solutions available in the market are listed in alphabetical order below:
-
Arista NDR
-
Blue Hexagon
-
Cisco StealthWatch
-
Darktrace
-
ExtraHop Reveal(x)
-
IBM QRadar
-
IronNet
-
LogRhythm
-
RSA NetWitness
-
Vectra AI
How Do You Integrate a Network Detection and Response Solution?
NDR solutions are often used in conjunction with other security solutions as part of a more comprehensive approach.
NDR solutions can be integrated with existing systems. These technologies offer efficient network threat detection while causing less friction with SOCs. Relying on sensors implemented off of a SPAN or TAP port, NDRs can passively monitor network traffic. How you integrate an NDR tool with other cybersecurity solutions such as, SOAR, SIEM, or cloud and enterprise networks are explained below:
-
NDR Integration with SOAR: Many NDR integrations occur within large enterprises with mature SOCs who prefer to leverage their own playbooks and workflows for a response. Therefore, many NDR vendors provide integration with SOAR platforms from vendors such as Splunk, and Swimlane.
-
NDR Integration with SIEM: SOCs can seamlessly integrate NDR solutions with SIEMs, enabling full visibility within existing workflows, while still enabling a shift into the NDR as required for deeper analysis.
-
NDR Integration with workloads in public or private clouds: With many enterprises moving data and workloads to the cloud, integrating NDR capabilities across public cloud, private cloud and hybrid cloud environments makes a lot of sense. Such integration makes it possible to monitor network activity across many domains, offering thorough protection.
-
NDR Integration with company networks: While delivering network threat detection, NDR systems are designed to bring little complexity to SOCs. NDRs use sensors launched from a SPAN or TAP port in order to passively monitor network traffic.
How Did Network Detection and Response Evolve?
In 2020, with the release of the Market Guide for Network Detection and Response, Gartner first identified NDR as a distinct cybersecurity category. NDR has gained significant popularity in recent years and is quickly becoming an essential cyber security tool for enterprises.
Indeed, NDR is one of the three pillars of Gartner's SOC Visibility Triage security architecture, alongside Security Information & Event Management (SIEM) and Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR). NDR delivers crucial network data that complements the other pillars to give security professionals total insight into threats.
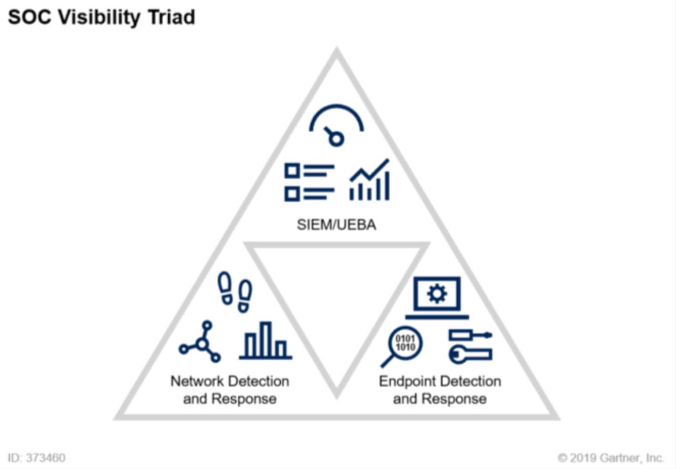
Figure 2. SOC Visibility Triad
With the unveiling of the SOC Visibility Triad, Gartner says that:
"Due to the increasing complexity of threats, companies must utilize numerous data sources for threat detection and response. Without utilizing agents, network-based solutions allow technical experts to acquire rapid threat awareness across an entire ecosystem. "
Keeping an eye on network traffic is not a new thing. In the beginning, network metadata was collected to study how the network operates well. But as the amount of data grew, many organizations were unable to use network activity to their advantage, leaving it as a cyber defense resource that wasn't being used.
Eventually, computers became powerful enough to keep up, giving companies the ability to see network traffic and use behavioral analysis to find security holes. This technology was first called network traffic analysis (NTA). Even though NTA is still used in enterprise security operations centers (SOCs), the market category has changed and grown to include network detection and response. Organizations are putting more value on NDR solutions' ability to respond to threats found by network traffic analysis tools, which mostly focus on threats that can only be found and are mostly simple variations of known threats.
NDR solutions are now based on increasingly advanced behavioral analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence (AI) of cloud, virtual, and on-premise networks. By using these technologies, NDR vendors have helped organizations improve their ability to find threats, figure out how confident and risky they are, and automate more and more of the tasks that analysts used to do manually, such as getting relevant third-party contextual telemetry information and using standard investigative playbooks to further rank threats by risk, so that they can focus on triage and rapid response. With the help of machine learning models, advanced NDR tools can find both known unknown cyber threats and brand new zero-day threats.
Monitoring network traffic for attacks enables security teams to identify active attackers as early as feasible in the attack lifecycle. Nevertheless, despite their advantages, NDR tools have their limitations. They are only capable of analyzing network logs and cannot monitor or track endpoint events, such as process information, registry changes, or system commands. They are unable to investigate cloud or identity data or other vital security information sources. Multiple data sources must be analyzed in order to identify and confirm malicious activity in the event of a complex attack. Costly to deploy and maintain, siloed cybersecurity tools like NDR solutions create possible blind spots and require security analysts to switch between consoles to obtain context.
Traditional network detection and response systems are exclusively concerned with network data. This limited area of analysis can lead to missed detections, an increase in false positives, and prolonged investigations. These flaws exacerbate the issues that many security teams already face, such as too many siloed technologies, too many warnings, and insufficient time.
What is the Difference Between EDR and NDR?
EDR is an abbreviation for endpoint detection and response. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) is meant to detect and defend against endpoint attacks that typically target network endpoints, such as computers, phones, and servers. Additionally, an EDR may provide analytics, a context for the analytics, prevent potentially harmful activity, and restore the system. Rather than being a single application or program, an EDR is generally a system composed of components that perform distinct security duties. Antivirus software, automated analysis, and forensic solutions, endpoint monitoring, and administration, and security team alert systems are examples of the components. With these tools, an EDR is capable of efficiently preventing occurrences, mitigating immediate danger, and remediating the situation after an incident.
Similar to EDR, NDR utilizes a toolset of sophisticated automated algorithms to avoid cyber events, reduce existing threats, remediate any potential network breaches, and alert the security team of network discoveries. NDR may be cloud-based, on-premises, or virtual, and it uses machine learning to discover unknown and recognized network risks. NDR examines the totality of network traffic to acquire visibility into potential cyber threats, offering real-time network visibility. These tools complement one another nicely, although many businesses are not adopting NDR as well as they could.
EDR and NDR exist at the workplace in order to record and monitor, provide analytics, inform the team of suspicious activity, and prevent a potential cyber crisis. The distinction between EDR and NDR is that NDR monitors communications inside itself, resulting in real-time network visibility. EDR focuses on monitoring and preventing endpoint assaults, which often target PCs and servers. Because of this, EDR may overlook devious cybercriminal attacks, but NDR can identify them. EDR is the ground-level perspective of the system, while NDR is the aerial perspective. NDR is regarded as more complete than EDR, although its configuration may be much more complicated and costly. For this reason, most SMBs opt for EDR rather than NDR.
Whether EDR or NDR is a better match for your organization, it is essential to have both since they provide 24/7 preventive, immediate, and post-incident cyber protection. The automatic features of EDR and NDR save your cybersecurity team time and money and provide them with important warnings and analytics in real-time, allowing them to comprehend and repair system vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
What is XDR?
Extended detection and response, or XDR, is a novel method for detecting and responding to threats. XDR broadens the scope of security beyond a single data source, such as endpoint, network, cloud, or identity data, realizing that investigating incidents in isolated silos is ineffective. XDR platforms automatically combine data from various sources and employ artificial intelligence (AI) to detect undetected cyber threats. Compared to standalone security technologies, this improves visibility and efficiency. Consequently, investigations across security operations are streamlined, lowering the time required to discover, verify, and respond to assaults.
Forrester Research says that XDR is:
"The evolution of EDR, which optimizes threat detection, investigation, response, and hunting in real-time. XDR unifies security-relevant endpoint detections with telemetry from security and business tools such as email security, network analysis, and visibility, cloud security, identity, and access management, and more. It is a cloud-native platform built on big data infrastructure to provide security teams with flexibility, scalability, and opportunities for automation."
Gartner recommends:
"Extended detection and response define a unified security incident detection and response platform that gathers and correlates data automatically from many proprietary security components. Leaders in security and risk management should evaluate the risks and benefits of an XDR solution."
What is the Difference between XDR and NDR?
NDR and XDR both aim to assist businesses in detecting and responding to threats. The essential distinction is in the data source, the analytic technique, and the requirements required to get value from the various data sources.
| NDR | XDR | |
|---|---|---|
| Data Source | - Traffic mirror, - Network tap, - Cloud flow logs (on premises, virtual, hybrid, or public cloud) | -NGFW appliances analyzing network traffic, - Combination of endpoint agents analyzing host process behavior, - other data sources |
| Deployment Location | - Data center, - Out-of-band in cloud, - Remote sites, - No agents | - Agents on each endpoint, - NGFW appliances both internally and at perimeter for greater visibility |
| Deployment Method | Low deployment friction | High deployment friction |
| Performance Factors | No negative performance impact | When monitoring east-west traffic, performance is impacted |
| Core Approach | Best in class: To prevent vendor lock-in, a purpose-built NDR for passive monitoring of L2-L7 network traffic that employs machine learning and is natively connected with threat intelligence data, SIEM, and EDR. | XDR solutions are often vendor-specific, restricting third-party connectors to data enrichment such as threat intelligence feeds. |
Table 1. NDR vs XDR
| XDR | EDR | NDR | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | Endpoints, hosts, network, and inter-device traffic and finally applications | Endpoints and hosts | Network and inter-device traffic |
| Intention | Visibility/transparency at many security layers (network, endpoint, apps), identification of known and unknown threats, vulnerability assessment, alerting and response, holistic monitoring and mitigation, consolidation and simplification of events, and actions and targeted reaction. | EDR prioritizes endpoint and access area security. This is the result of infiltration, monitoring, mitigation, vulnerability assessment, alerting, and reaction. | The visibility and/or transparency of network traffic in addition to the detection of known and unknown risks and lateral movement, alerting, and action. |
| Methods | - Machine learning,- Techniques and Procedures (TTPs),- identification of attacker Tactics, - Malicious behavior detection,- anomaly detection, and - analysis of Indicators of Compromise (IoCs). | - TTP analysis,- Indicator of Compromise (IoC) analysis,- Malicious behavior detection,- signatures, and machine learning. | - Indicator of Attack (IoA),- machine learning.- Anomaly detection,- user behavior |
| Challenges | Integration with other vendor solutions. | Advanced Persistent Threats (APT), ransomware, and more. | Advanced Persistent Threats (APT), ransomware, and more. |
Table 2. XDR vs EDR vs NDR
Network Detection and Response vs. Network Traffic Analytics
A lot of the confusion about NDR comes from the fact that it is connected to network traffic analytics (NTA). The process of gathering and analyzing network traffic is called NTA. NDR is a part of the NTA set.
Network traffic analysis, or NTA, is the process of keeping an eye on the availability of a network. NTA can spot unusual activities that could mean there are problems with operations or security. By keeping a record of what is happening now and in the past, the NTA can find operational problems like network slowdowns. NTA can find problems, like malware attacks and the active use of protocols and ciphers that can be broken. By making it easier for people to see what's going on inside NTA, these blind spots can be eliminated.
There are many ways to deal with NTA, but the best way is through NDR.
NDR adds built-in response capabilities to the real-time monitoring and analysis that NTA already does. The most complete NDR solutions use security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) technology to make response options easier to use and automate.
What is the Difference Between NDR and IPS?
Intrusion Prevention Systems(IPS) use their exploit-facing pre-programmed signatures to alert administrators, delete malicious packets, ban access from problematic source addresses, and reset connections.
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) with its hundreds of signature-based detections sometimes misidentify innocuous activities as hostile and generate false alarms. False positives waste the work of security analysts and may lead to alert fatigue, which increases the probability that a legitimate alarm will go uninvestigated, allowing a preventative breach to occur.
Systems in the Network Detection & Response (NDR) category assist security teams in precisely identifying and investigating harmful actions, as well as triggering automatic responses to genuine threats with a far lower probability of false positives than IPS products.
Due to their tendency to generate false warnings, Intrusion Prevention Systems cannot always assist SOC teams in distinguishing signals from noise. New signatures must be produced, which is a labor-intensive and time-consuming process that requires human participation. As a result, IPS systems may struggle to identify new or developing threats. This possible time lag between discovering new threats and developing unique signatures might provide fast and innovative attackers the advantage they need to remain two steps ahead of protection. It might be difficult for an IPS solution to evaluate encrypted data without decryption tools.
Network Detection & Response security technologies rapidly decode dozens of protocols and extract hundreds of machine learning characteristics in order to identify late-stage attack activities with context and evidence to support a confident response.
Because NDR solutions employ machine learning to develop predictive behavior models rather than relying just on signatures as a baseline for detection, they may identify never-before-seen security risks and often-missed low-and-slow strategies, approaches, and processes.
If you currently use an IPS solution, NDR systems give richer data that may minimize the number of false warnings and shorten the time required to discover threats.
