Bluetooth in Cyber Security: Understanding Bluetooth Attacks
Bluetooth is a standard for short-range wireless connections between electronic items. Ericsson introduced the concept in 1994, and consumer electronics quickly adopted it. Bluetooth devices connect with one another without maintaining an optical path of vision since the technology uses radio waves to accomplish that. It takes advantage of the unlicensed, low-power GHz spectrum, which is accessible anywhere. For the needs of diverse electrical devices, Bluetooth technology offers developers a flexible range of full-stack, adequate solutions. Its primary characteristics include minimal power consumption, easy battery operation, and a reasonable price.
Over time, Bluetooth technology has undergone significant development. From switching out of cables to low-energy and then mesh technology, Bluetooth technology has advanced, and numerous versions of Bluetooth have been developed. The newest version of Bluetooth, Bluetooth5, offers less battery usage without losing range. Bluetooth Low Energy (LE) enables the development of dependable, large-scale device networks by supporting a variety of communication topologies, ranging from direct to broadcast and, most recently, mesh. A large majority of modern electronics, including computers, smartwatches, headphones, speakers, and smartphones, use Bluetooth technology. After the first mobile phone with Bluetooth features hit the market in the millennium in the mid-2000s, the technology became far more common.
Bluetooth is a popular wireless connection technology, yet it has an expected number of weaknesses that make it vulnerable to cyber-attacks. In the context of cyber security, understanding Bluetooth attacks is crucial since attackers use weaknesses to get unauthorized access to sensitive data or take over devices. Bluejacking, bluesnarfing, eavesdropping, denial of service attacks, viruses, and worms, Bluetooth headset vulnerability, and unauthorized device access are a few typical Bluetooth attacks. Additionally, BlueSmacking, BlueBugging, Bluetooth Low Energy Spoofing Attacks (BLESA), Bluetooth Impersonation Attacks (BIAS), KNOB and BLURtooth attacks, and the Bluetooth BrakTooth family of attacks are other versions of common Bluetooth attacks.
To provide a better understanding, one of the most common Bluetooth attacks, known as bluesnarfing, allows the attacker to access any files on the victim's device if the victim's Bluetooth driver installation is done improperly. Another frequent attack is called bluejacking, in which the perpetrator overwhelms Bluetooth-enabled devices through unsolicited messages. Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks are a further possibility, in which a perpetrator intercepts a Bluetooth connection between two devices that believe they are communicating straight away with one another.
The following topics are going to be covered in this article;
-
What is Bluetooth in simple words?
-
What is Bluetooth and how does it work?
-
What is the difference between Wi-Fi and Bluetooth?
-
Is Bluetooth using Wi-Fi?
-
What are the benefits of Bluetooth?
-
What are the challenges and limitations of Bluetooth technology?
-
What is a Bluetooth attack in cyber security?
-
What are the future developments and trends in Bluetooth technology?
-
How is Bluetooth used in Internet of Things (IoT) devices and smart home applications?
-
What are the potential vulnerabilities and risks associated with Bluetooth?
What is Bluetooth in simple words?
Eliminating the use of cables, Bluetooth is a wireless technology that enables communication between devices across short distances using radio frequency. Bluetooth is frequently used to link mobile devices with fixed or stationary devices, including headphones, vehicles, and smart refrigerators. Bluetooth technology has made it easier to complete tasks that previously necessitated tangled wires in peripheral devices. Because Bluetooth waves are short-range and continuously changing frequencies, it is challenging for hackers to eavesdrop on the signal. Bluetooth subsequently gained enormous popularity in consumer electronics in time due to the advantages it brought, including being easy to use, inexpensive, and employing a standard protocol.
As a practical method for wireless data transport, when compared to radio stations, Bluetooth employs radio waves to communicate data between devices, however, those waves have a limited range. This implies that for devices to remain connected, they must be close to one another. In order to prevent hackers from intercepting the signal, Bluetooth uses a method known as "frequency hopping spread spectrum" to switch frequencies continuously.
Ultra-high frequency radio waves with wavelengths of 2.4 gigahertz are used by Bluetooth devices. When two devices with Bluetooth capability are in close proximity to one another, they immediately recognize and pair with one another, enabling wireless data transfer. Wi-Fi and Bluetooth both operate in the same limited band of frequencies, but Bluetooth consumes significantly less power, so there is very little interference with a Wi-Fi connection. Bluetooth technology encrypts and decrypts data into packages using algorithms known as codecs to facilitate data transmission.
There are numerous Bluetooth products that can be used in daily life, including wireless gates, smartwatches, stereos and headsets, mobile phones, health sensors, safety trackers, and workout equipment, which are just a few of the gadgets that employ Bluetooth. Gaming controllers, remote controls, file-sharing tools, and multiplayer mobile games all use Bluetooth technology to connect wirelessly.
Some of most common use cases of Bluetooth in time are as follows;
-
Mobile phones via hands-free headset communication.
-
Controlling music and communication features wirelessly between a smartphone and a Bluetooth-enabled car radio system.
-
Smart locks and smartphones can communicate wirelessly to unlock doors.
-
Controlling and communicating wirelessly with mobile phones, tablets, and wireless speakers.
-
Intercom and a wireless Bluetooth headset.
-
Wireless audio stream to headphones.
-
Wireless data transfer from Bluetooth-enabled fitness equipment to a phone or computer.
-
Wireless networking between computers in a small area with minimal bandwidth usage.
-
The most popular computer input and output devices include the mouse, keyboard, and printer.
-
Theft and man overboard alarms by constantly checking range.
-
Real-time location systems (RTLS) including traffic divisions to share information about travel times and backed-up traffic.
-
Wireless data transmission from workout equipment with Bluetooth functionality.
-
Wireless networking between computers in a small area with minimal bandwidth usage.
-
PC input and output devices, such as the mouse, keyboard, and printer.
-
Files, contact information, calendar events, and reminders share and transfer.
-
Smartphone selfie sticks control.
-
Controlling and communicating wirelessly with mobile phones, tablets, and wireless speakers.
-
Intercom and a wireless bluetooth headset.
-
Wireless audio stream to headphones.
-
Wireless data transfer from Bluetooth-enabled fitness equipment to a phone or computer.
-
Test equipment, GPS receivers, medical equipment, barcode scanners, and traffic control devices, wired cable serial connections.
-
Using Bluetooth technology instead of infrared controllers.
-
For low bandwidth applications where a cable-free connection is preferred but larger USB bandwidth is not necessary.
-
Health sensor data from medical devices to mobile phones across a short distance.
How does Bluetooth Work?��
Bluetooth uses non-ionizing electromagnetic waves in the radio frequency band between 2.40 GHz and 2.48 GHz as a low-power, short-distance radio transmission system. To convert data into a format that can be transferred by Bluetooth, the Bluetooth signal is first processed by software using a compression mechanism known as a codec. To "pair", or link, neighboring devices, Bluetooth uses short-range radio waves. A computer chip in devices with Bluetooth functionality transmits a signal, so Bluetooth devices can identify one another in this way.
Speaking of Bluetooth range, the maximum communication distance varies depending on the environment and device class. The maximum range for Class 1 devices is up to a hundred meters; Class 2 devices are limited to ten meters; and Class 3 devices are limited to 1 meter. However, for the majority of devices, the Bluetooth connection's range is around ten meters. Depending on the electromagnetic environment or barriers, the maximum distance for communication will change. You can achieve a range of up to a hundred meters outside, in a wide-open space, although that is an uncommon circumstance. Obstacles like concrete walls in a household can considerably restrict the distance.
Various integrated elements of Bluetooth technology enhance the technology's security are listed below;
- Adaptive Frequency Hopping: Bluetooth's frequency hopping employs the 2.4 GHz ISM band, which has 79 channels and allows for hops at a rate of 1600 per second. Existing frequencies are omitted from the hopping. Jamming and interference are both reduced by the ability to frequency hop.
- Pairing: Pairing permits communication between devices. For a pairing request to be made, the BD_ADDR of the device must be known. The BD_ADDR, which is covered in the previous two sections, is determined through scanning or knowledge of prior pairing.
- Undetectibility: Devices must be undetectable in order to respond to scanning attempts. The 48-bit BD_ADDR address of a device is also hidden.
- E0 Cipher Suite: The cipher typically uses stream ciphering and has a key length of 128 bits.
What is the Difference between Wi-Fi and Bluetooth?
WiFi is a wireless technology that uses a WiFi router to connect devices to the internet. In order to enable devices like computers, tablets, mobile phones, and notebooks with internet access, an internet service provider transmits a WiFi signal to the router. The flow of data between these devices will then result in the creation of a WLAN. The network's coverage area is between 50 to 90 meters.
Both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi employ radio waves for communication, but they serve various goals and have distinctive properties. While Wi-Fi is used to connect devices to the internet, Bluetooth is primarily used for short-range data transfer between devices, such as between a mobile phone and wireless headphones. Among many other things, Bluetooth enables you to wirelessly link your keyboard and mouse to your notebook, your headphones to your phone, a speaker's volume through an app on your phone, and your phone to the vehicle's sound system. When you "pair" Bluetooth wireless devices, an exchange between the devices happens right away. Establishing trust between gadgets and determining whether data sharing is necessary are the objectives of the exchange. Your signals won't interact with other signals nearby due to the Bluetooth FHSS(Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum) technology.
While the range of Wi-Fi networks is often greater than that of Bluetooth connections as well, Bluetooth does away with the need for a wired connection while still ensuring an accessible line of sight for transmission between electronic gadgets. In order to increase the signal's bandwidth for data transfer, Wi-Fi splits a signal into fragments and sends those pieces over a variety of radio frequencies. Wi-Fi operates at frequencies between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz.
Is Bluetooth using Wi-Fi?
No. Bluetooth does not use Wi-fi for data transmission. As it employs radio signals, there is no need for Wi-Fi or connection to the internet to be established or used. The majority of Bluetooth devices can, however, also connect to the internet.
What are the Benefits of Bluetooth?
There are numerous fields where Bluetooth technology is employed. A few of many applications and use cases for Bluetooth technology includes;
-
Multiple devices being charged simultaneously through energy transfer
-
Embedded tags for tracking personal effects and baggage at airports
-
Guided museum tours
-
Electronic shelf labels
-
Wireless audio streaming
-
Remote controls
-
File syncing and sharing between platforms
-
Mobile multiplayer games
-
Retail
-
Location tracking and medicine
The following are just a few advantages of Bluetooth technology:
-
Simple integration and connection setup.
-
Wireless connection, which takes away the need for wiring.
-
It uses a limited amount of power, therefore, becoming energy-efficient.
-
The noise from other wireless devices is kept to a minimum.
-
Easy access and ease of use, as many gadgets already have Bluetooth embedded.
-
Cost-effectiveness, as Bluetooth gadgets are more affordable than competing models.
-
Ability to connect multiple devices simultaneously.
-
Rapid connection establishment with the help of Bluetooth's instantaneous creation of ad hoc connections.
-
Since Bluetooth is the industry-standard wireless protocol, it works well with almost all wireless devices, regardless of brand or model.
-
Few devices within a close range can create a small Bluetooth network.
-
You must manually approve all new connections whenever you are utilizing Bluetooth to connect to a device for the first time. This helps lower the chance of unidentified users connecting to your device, while it's still possible for someone to intercept your connection.
-
It's widely used around the globe.
What are the Challenges and Limitations of Bluetooth Technology?
Performance, compatibility, and user experience problems can arise with Bluetooth technology. When there are several devices present, Bluetooth connections are challenging to establish. When earlier and more modern Bluetooth versions attempt to communicate with one another or with a different device, compatibility problems occur. It's possible that manufacturers won't be able to foresee potential compatibility problems that might occur when interacting with devices from other companies running variously customized versions of Bluetooth. Devices occasionally fail to function together. This indicates that your keyboard, for instance, won't communicate with your PC regardless of what diagnostic measures you take. Reaching out to their user manuals to determine if they are compatible may be helpful to get around the situation.
Bluetooth technology presents potential cybersecurity risks when utilized with medical equipment. Hackers looking to obtain data may potentially use Bluetooth security flaws as a tool. Some known drawbacks of Bluetooth technology are listed below:
-
Distance limitations while communicating between devices
-
Limited bandwidth
-
Connection failure under particular circumstances
-
Susceptibility to interference and security issues due to Bluetooth's hackability
-
Slower data transfer rates than those offered by Wi-Fi and other wireless communication technologies
-
When compared to a wired connection, Bluetooth may drain your battery more quickly
-
Finding other Bluetooth devices nearby is simple with the advent of Bluetooth technology, even if you've never connected with them before
What is a Bluetooth Attack in Cybersecurity?
Bluetooth hacking is a method for obtaining data from another Bluetooth-enabled device without the host's knowledge or consent. A cyber-attack of this kind that targets Bluetooth-enabled devices is called a Bluetooth attack. A Bluetooth attack has adverse implications. A motivation for hackers who gain access to a device via a Bluetooth attack can be stealing confidential data, observing the user, or even imitating their identity. Attacks on Bluetooth take many different forms, such as bluesnarfing, bluejacking, and bluebugging. The most common Bluetooth attacks are outlined below:
- Bluesnarfing: In a bluesnarfing attack, the victim's Bluetooth software for drivers is vulnerable, allowing the hacker to access all data on the victim's device. It has the power to turn off the battery or disable the device's features or even the device itself.
- Bluejacking: In a different scenario, when a Bluetooth device uses spam advertising to hijack another, is known as bluejacking. It may result in the installation of malware or the transfer of undesirable data.
- Bluebugging: In a bluebugging attack, a cybercriminal uses a covert Bluetooth connection to acquire backdoor access to your device, allowing them to eavesdrop on you and access your personal information. In some circumstances, a hacker uses a Denial of Service attack to overwhelm and disable a Bluetooth-enabled device. A hacker may potentially be able to obtain confidential information and pose as the user.
- BlueSmacking: A denial of service (DoS) attack called "BlueSmacking" aims to overwhelm your device and shut it down. Large data packets are sent to your device by cybercriminals to penetrate. Once your device is turned off, hackers will use BlueSmacking as a launchpad for more serious attacks. Once restarted, your device will usually get back to normal.
- Car Whispering: Another Bluetooth security flaw known as "car whispering" attacks automobile radios with Bluetooth functionality. Hackers employ this method to listen in on phone calls as well as conversations inside the vehicle. In other instances, the hackers can make use of the link to maliciously inject audio into the vehicle in another instance.
Despite precautions to safeguard it, Bluetooth is still vulnerable to hacking attacks. Bluetooth authentication does not guarantee that the distant device is safe; it just verifies that the user is connected to the device they believe they are. Users should make sure their devices have the most recent security updates installed and use strong passwords to reduce the potential risks. Users should disable Bluetooth on their devices if they have to, refrain from sharing sensitive information via Bluetooth, and decline any unauthorized connection requests in order to reduce the potential risk of Bluetooth attacks. The Bluetooth SIG has put programs in place to address usability problems and enhance interoperability.
How is Bluetooth used in Internet of Things (IoT) Devices and Smart Home Applications?
As Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology that enables data transmission between two electronic devices over a short distance, many Internet of Things (IoT) devices that fit this description employ Bluetooth technology. Smart door locks, smart lighting, HVAC systems, wireless speakers, LED light bulbs, smart thermostats, smart home appliances, and any smart wearables are a few examples. IoT device capability is being increased more effectively using Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) technologies compared to the internet. In comparison to a Wi-Fi network, BLE can nearly quadruple the range of a device's connection. When used indoors and in pairing with IoT devices, Bluetooth is a well-rounded tool for communication in "noisy" environments at low bandwidth.
Although it provides many advantages to daily users, potential vulnerabilities and interoperability issues may exist. Interoperability across various devices and manufacturers still faces difficulties despite the standardization of Bluetooth protocols and profiles. The capacity of Bluetooth devices from various manufacturers to easily connect with one another is referred to as Bluetooth interoperability. The interaction between radio and baseband decoders, as well as the interfaces between baseband and protocols, is one of the primary problems. Additionally, Bluetooth support varies between devices, which can cause interoperability problems. Initial pairing and connection establishment might be unreliable as well, which may cause discomfort for the users.
Standardized protocols and profiles are utilized to accomplish this, ensuring that devices can recognize and comprehend each other's signals. In order to build large-scale device networks that provide secure, dependable communication across many hundreds of devices, interoperability is a benefit of standardization across every tier of the complete communications stack.
Interoperability problems are identified and fixed using interoperability testing tools like the Bluetooth Test Platform (BTP) and Bluetooth RF sniffers. To mitigate and minimize interoperability problems, Bluetooth uses established protocols and profiles to guarantee interoperability. This enables easy communication between gadgets made by various manufacturers. The "5-Minute Ready" program, which strives to address usability concerns and make sure that devices are simple to use and connect with one another, is one of the projects that Bluetooth SIG has developed to increase interoperability. The Bluetooth Test Platform (BTP), which automates typical scenarios crucial for Bluetooth hardware, drivers, and software, is one example of an interoperability solution that is accessible. Interoperability problems can still occur, but there are tools for diagnosing and fixing them, such as Bluetooth RF sniffers.
What are the Potential Vulnerabilities and Risks associated with Bluetooth?
We expect our personal information to be kept private when we use our electronic gadgets, including smartphones and other mobile devices. We believe we have complete control over who can see or hear what we're doing when we make a call, send a text, or browse the internet. But in actuality, you could never know if someone is eavesdropping.
KNOB (Key Negotiation of Bluetooth) enables hackers to put themselves in between two Bluetooth-connected devices, giving them the power to eavesdrop on calls and nearly all transmissions of data. It has the ability to inject its own data and might thus be used to spread malware on devices. The fact that KNOB attacks are absolutely undetectable is much more concerning.
Particularly when your Bluetooth device is discoverable and doesn't require a security code, someone may connect to it without your permission. However, this scenario is unlikely, as modern Bluetooth devices require some sort of pairing procedure before a successful connection. Yet the possibility is not completely off the table considering today's advanced hacking mechanisms. You can disable automatic connect or pairing functions on your device, turn off Bluetooth when it's not in use, and avoid pairing devices in public places to prevent intrusive access.
A hacker might be able to intercept any data exchanged between two infected devices and even send their own data, which might contain viruses and other dangerous programs. However, because Bluetooth is used, the hacker would need to be within the proper wireless range, which would require them to be close to their target.
Encryption and validation problems are mostly the root of the weakness. The typical small business owner is unlikely to want to spend time educating themselves on this kind of technical knowledge; instead, what they truly need to know is whether they are affected and what they can do to protect themselves.
There are a few ways to check if someone has connected to your Bluetooth device without your knowledge. You can look for a list of associated devices by going through the Bluetooth settings on your device. It might be a sign that someone has connected to your device if you see a device that you are unfamiliar with. Additionally, you can regularly check your Bluetooth connections to make sure everything is functioning properly.
Security experts found a similar weakness in past years, which gave manufacturers time to develop security solutions. Following the attacks, some suppliers added patches to their products to address the issue. Although they've taken action to fix the problem, it doesn't necessarily mean all devices are safe, considering device update statistics in general. As a result, it's crucial to keep the devices up to date due to the possibility of a software fix at any time.
Nevertheless, when it comes to mobile phone attacks, Bluetooth attacks are really the surface of the spear; there are numerous additional ways that hackers might snoop on your phone including Wi-Fi hacking, Websites, email attachments, rogue apps, eavesdropping devices, SIM cloning, and shoulder surfing, etc. These methods enable them to gain access to your phone's camera, photographs, files, contact list, and calls.
What are the Signs of Bluetooth Attacks?
Since Bluetooth attacks are intended to be undetectable, they can be challenging to spot. The following are some typical indicators that your phone has been exposed to third parties:
-
General slowdown and poor performance of your device
-
Unfamiliar applications or programs downloaded to your device
-
Unexpected network activity including higher consumption of data
-
Attempts to access your online accounts without your permission
-
Unknown Bluetooth connections to your device
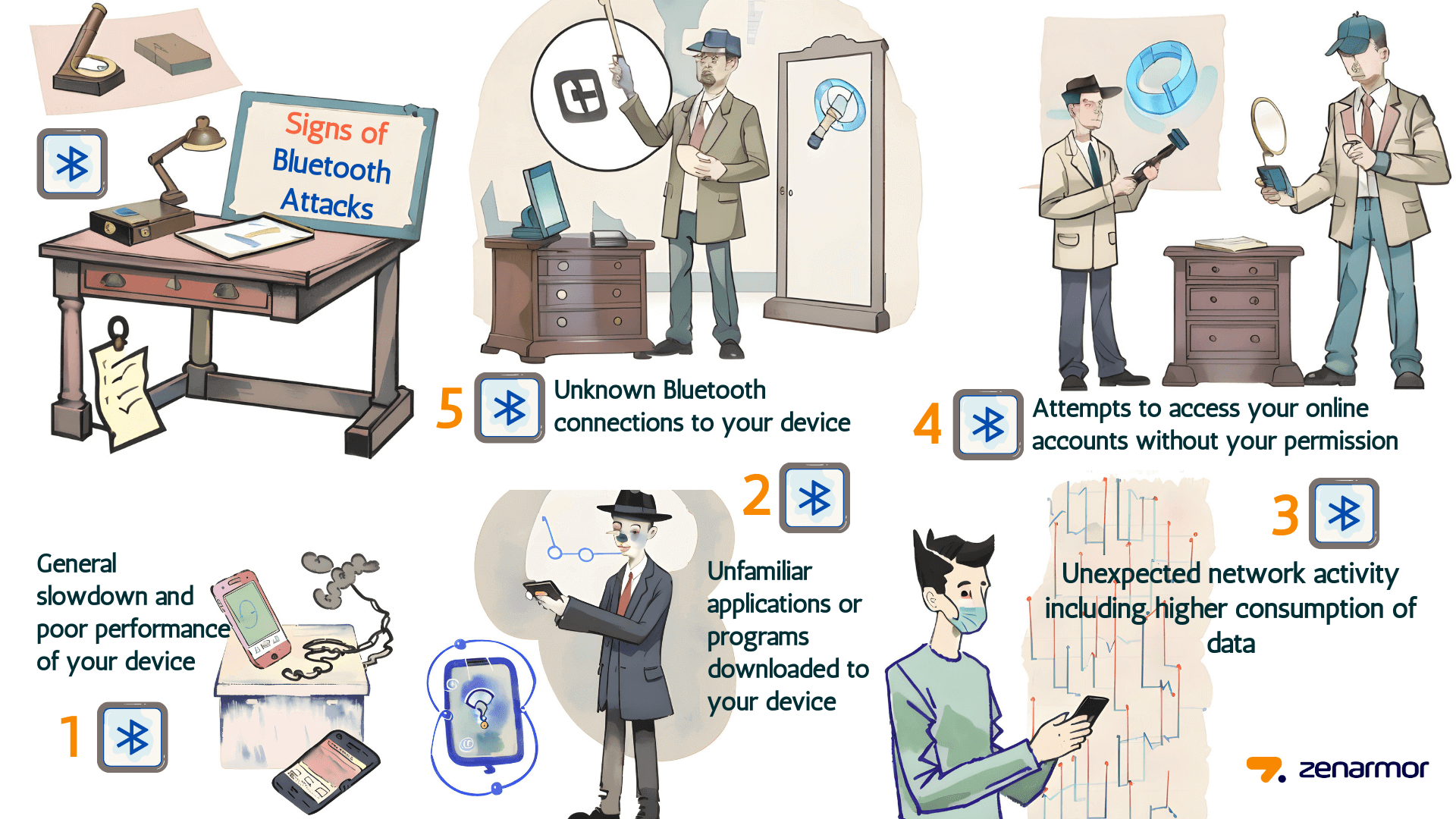
Figure 1. Signs of Bluetooth Attacks
How to Prevent Bluetooth Attacks?
In order to provide entry-level protection to your device against Bluetooth attacks there are some simple but effective methods to employ, including;
-
Don't set up pairing via public connections. Always pair two devices from a secure location when doing so for the first time.
-
When not in use, turn off Bluetooth.
-
Steer clear of Bluetooth while exchanging private information.
-
Be cautious about who you share your Bluetooth connection with.
-
Always update your operating system and drivers if needed.
-
Removing previous unnecessary Bluetooth connections is advised.
-
Ensure that your device is untraceable.
-
To prevent Bluetooth spying, set your Bluetooth device to "undiscoverable" mode.
Another concept to discuss in Bluetooth security is pairing and bonding procedures. The process of pairing involves generating one or more shared secret keys for use by two devices. It is the system that makes bonding possible. On the other hand, bonding is the process of storing the keys generated during pairing for use in later connections to create a trusted device pair. After pairing, it involves exchanging long-term keys and storing them for later use. In other words, bonding is the procedure where the information from the pairing process is saved on the devices so that the pairing process does not have to be performed every time. Pairing is the exchange of security characteristics each device has, establishing temporary encryption.
Both Bluetooth technology and Bluetooth-connected devices are subject to a wide range of security vulnerabilities. For this reason, users should be aware of the hazards associated with using Bluetooth technology on their devices as well as the mitigation strategies that may be employed to keep their devices and data safe from hackers. By putting into practice the security recommendations, Bluetooth-related threats can be reduced. Each individual should be in charge of protecting their Bluetooth communications.
How to Configure Bluetooth in a Secure Way?
You can also follow these methods to make your Bluetooth more private:
-
Go to Settings > Privacy > Bluetooth Sharing on your device, then slide the switches next to any permitted apps to the "Off" position to disable Bluetooth sharing.
-
Completely deactivate Bluetooth on your device.
-
Use your mobile device's Bluetooth in "hidden" mode.
-
On your Bluetooth device, turn off the "Discoverable" option and "Sharing" options.
-
Your mobile device should be set to "not visible".
-
To find out whether any apps you download utilize Bluetooth to track your location, it's important to review the privacy statements for such apps.
What are the Future Developments and Trends in Bluetooth Technology?
Bluetooth technology is continually changing, with new developments and trends appearing frequently. BLE advances, enhanced security features, interoperability, and faster data transmission rates are some of the ongoing developments and significant progress in Bluetooth technology.
On the other hand, according to recent predictions, IoT technology will have a significant impact on the market for Bluetooth end devices by 2024. Some of the most recent advancements in Bluetooth technology that have created new opportunities is Bluetooth 5.4. The Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) has announced Bluetooth 5.4, the most recent version of Bluetooth technology. The Bluetooth SIG collaborates with many ongoing specification development projects on an ongoing basis. These projects could involve enhancing existing Bluetooth technology with small features as well as major functional additions. Hence, it is expected to see key specification projects with features that benefit different IoT industries. Real-time asset tracking is expanding quickly, thanks in large part to Bluetooth technology. Additionally, it is anticipated that the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) will keep expanding, data security will continue to be a top priority, and 5G will fuel IoT growth. These are a few of the Bluetooth technology trends that are just starting to take off.
More intelligent, connected devices will be needed to communicate with one another as IoT applications spread, functioning in environments with varying levels of range and cost requirements, user interactions, mobility, and energy constraints. For the Internet of Things (IoT) sector to take advantage of new market prospects, wireless solutions that can meet the previously mentioned requirements are essential. In order to allow dependable and scalable Internet of Things (IoT) networks where thousands of devices, including sensors, smartphones, wearable devices, robots, and daily appliances, function together, Bluetooth Mesh, an emerging wireless protocol, extends the basic Bluetooth low energy (BLE) stack.
The potential future directions and applications of Bluetooth technology include Bluetooth mesh networking and its impact on smart cities, smart industries, and IoT expansion. The idea of "smart cities" encompasses a variety of technologies and methods for gathering data from a city and sending it over a network for processing and analysis. Sustainability of the environment and residents are smart cities' top priorities. The most common strategy used in practice is the use of wireless sensor networks over mesh networks. When it comes to wireless communication technologies, Bluetooth Low Energy presents a reliable, affordable, and power-efficient alternative. The recently released Bluetooth mesh profile specification, which includes secure multicast communications capabilities, addresses the most important issues with that paradigm. A framework for developing services for smart cities has been established, and the adaptability of the specification to a signaling service was demonstrated. In order to help researchers and practitioners better understand how Bluetooth Mesh might be used in IoT situations, the proposed service demonstrated how data can be gathered and shared between devices in a mesh network over a metropolitan area.
Although the global pandemic negatively impacted supply chains and caused apparent temporary transportation shortages for some device types, including mobile devices, asset tracking devices, and speech-controlled front ends, and short-term projections are slightly lower than previous years, analysts expect higher growth over the following five-year projections. Recent industry analysis indicates that prospects exist in the consumer electronics, smart home, and healthcare sectors for the global Bluetooth low-energy IC market. From 2022 to 2027, the market for Bluetooth low-energy ICs is projected to expand by 20%. Over the same period of time, annual shipments of devices with Bluetooth technology are expected to increase from five billion to seven and a half billion.