What is Firewall Auditing?
The firewall is the security system of a network that has a check on the information being transferred to and from the network on the basis of an already determined set of rules. It creates a barrier between a trusted and an untrusted network.
The firewall system is categorized into two types; one is the network-based firewall and the other is a host-based firewall system. The most basic and primitive type of firewall is the Packet Filtering firewall.
A packet filtering firewall acts as a checkpoint at a switch or at the network router. The most secure type of firewall is the Proxy Server Firewall which is considered effective in protecting the network resources by filtering the transferred messages. Proxy Firewall keeps the IP address anonymous and limits the traffic flow between the networks.
A firewall audit is a procedure for gaining visibility into your firewall's current access and connections, as well as reporting on firewall adjustments and identifying vulnerabilities.
Security of a network is not a permanent entity, it is in fact an ongoing process that is to be updated regularly. A minor error can risk the whole network system hence it is very important to look out for these errors, upgrade the network systems, find solutions to fix these bugs, and then audit the security measures. This is the exact reason why the firewall auditing system is important.
What does Firewall Auditing Mean?
A firewall audit is a process that assists administrators in identifying vulnerabilities in the network and determining areas where security policies must be customized.
Firewall checks the messages sent across networks and blocks those messages which may not match with the security requirements and may appear inappropriate or as threats and harmful to the internet systems. Regular firewall upgradation is also necessary to keep up with the renewed policies. It is recommended to update your firewall system just as the security updates and patches are released.
Firewall auditing system checks on the vulnerabilities which may be present in the security networks and allows customization of securities in those areas where they may be required. It helps block traffic from unauthorized sources and prevent security threats to the internet networks and just make it all very secure.
Additionally, the firewall auditioning system is a major solution to deal with most dangerous and harmful codes such as malware.
What Advantages does a Firewall Audit Provide?
A firewall audit can yield the following advantages:
- Adherence to pertinent regulatory obligations, including but not limited to GDPR and HIPAA.
- Enhanced security by identifying and resolving vulnerabilities in security systems.
- Enhanced network performance through the detection and resolution of configuration issues that hinder network velocity and effectiveness.
- Preventing costly data intrusions and disruptions results in financial savings.
- Risk management through the assistance of organizations in comprehending their susceptibility and formulating approaches to mitigate weakness.
How Does Firewall Auditing Work?
As mentioned earlier that the firewall manages the security of the internet systems, it does so by blocking threats that may reach through unauthorized sources. How does it block traffic from such anonymous sources? Following are a few ways this firewall system works:
-
IP Addresses: An IP address identifies a device being used on the internet or a local network. Firewall filters out the traffic that may reach the internet systems through suspicious IP addresses.
-
Domain: The domain in the firewall refers to a profile of the network where the host system authenticates to a domain controller. A firewall system prevents the documents which may reach through threatening domains.
-
Ports: A port is a point through which the information can flow from a program on your device, from the internet to your device, or on another device in the network. Firewall auditing systems prevent the traffic that may be transferred through certain port(s) which are not recognized by the network system or appear to be threatening or harmful to the organization.
-
Content: Firewall systems also prevent the part of such documents which may contain inappropriate contents that may appear harmful to the security of the network. Texts or documents containing inappropriate or malicious keywords are blocked by the firewall auditing system.
What Does Firewall Auditing Do?
The firewall system maintains the security of the organization by keeping track of the data and messages being transferred to and from the network. The firewall auditing system manages the vulnerabilities of the security of the networks. It looks upon and reviews the messages being sent to and received by the private network. This helps in keeping the organization up to date by regularly checking the security controls which in turn enables us to respond to the security issues in a much better way. This firewall auditing system appears to be advantageous as:
- Once the firewall becomes functional, it is necessary to clean up and optimize it regularly or at least yearly. These annual audits are important for the protection of the network or of the organization as it proves to help find out the vulnerabilities of the system and fix them.
- The security policies of the organization have to be reviewed from time to time so that the security of the network is kept up to date and according to the current security policies. Setting up a firewall system is risky as it includes a lot of error possibilities that result in configuration errors and to manage these errors and keep continuous compliance, firewall audit tools come in handy.
How to Perform Firewall Auditing?
Firewall auditioning is the security system of a network that maintains its security by keeping a check on the messages being transferred to and from the network. It serves as a blockade between the trusted and non trusted systems.
Setting up a firewall system consists of many errors making it an error-prone task. Firewall systems help in protecting against the malicious payloads by detecting the unauthorized sources in a signature pattern. But with the rapid evolution of the malicious payloads, the signature pattern of detection of firewalls must also be updated regularly to deal with such malware.
For the proper functioning of the firewall system, it is necessary to follow a whole procedure. By following a few steps which are mentioned below, firewall auditing may be conducted.

Figure 1. How to Perform Firewall Auditing
1. Get Important Information
No audit is successful without collecting proper information regarding your system, be it it's hardware, software, network policies, or risks. The policies of the organization or the risks or vulnerabilities in a network system can be addressed only after the collection of relevant in-depth information of the organization. The following steps are needed to gain the correct information of a network:
- Having an overview of all the internet service providers (ISPs) and virtual network providers (VPNs).
- Review all the reports and documents of the previously held audits.
- Checking out the copies of the security policies of the network.
- Having access to the firewall logs for analytic purposes.
- Having complete vendor information concerning the operating system (OS) version, the default configuration, and even the recent patches.
Gaining all this information makes it easier to review the procedures with the relevant IT stakeholders and helps in tracking their impact on the network systems.
2. Assess the Change Management Process
Through a stable change management process, the firewall changes can be properly executed and traced. Inadequate change documentation and unreliable validation of the effects these changes have on the network give birth to countless issues. The change management procedures can be assessed by reviewing a few things which are as follows:
- How are the changes being tested? Is there someone who is enabled to make changes in the network system or are these changes being made from an anonymous or unauthorized source?
- How are those changes being approved? Is there someone deployed to approve the changes or is there a glitch in the security system which is granting unauthorized approval?
- By whom are those changes being implemented? Are those changes in the network or organization being made by authorized personnel or are they being made from an external unauthorized source?
- Do they possess the necessary documentation and authorization to submit change requests for the firewall, which may include VPN and subnet configurations?
- Is the business justification for the change, including any repercussions on network devices and topologies, documented?
- Were approvals documented prior to the implementation of the change?
- Do appropriate reviewer and approval signatures (physical or digital) exist in accordance with ISO and HIPAA regulations?
- Are the modifications thoroughly documented in the change ticket, encompassing any necessary remediation or cleansing efforts?
- Is the change window and/or installation date documented for every change?
- Do all approvers possess the necessary authorization to authorize modifications to the firewall (a list of authorized individuals, including firewall administrators, must be requested)?
- Does the modification have an expiration date?
- Is risk analysis documentation available for every change that entails the prioritization and aggregation of risks?
- Is the security posture of the target system taken into account, encompassing prospective cyberattacks?
To ensure that the firewall changes are being made formally, it is important to know how the changes are accordingly being requested, reviewed, approved, and implemented.
3. Audit Operating System, Evaluate Physical Security
By auditing both the operating system and physical security it is possible to neutralize the common cyber threats. For this, the following procedures are implemented:
- Having controlled access for the security of both the firewall and management servers.
- Evaluating the implemented device administration procedures.
- Having a regular check on the operating system to pass the standard checklist.
- Performing verification on the implementation of vendor patches and updates.
- Maintaining a list of the authorized people deployed to access the firewall server rooms.
4. Clean Up and Enhance the Rule Base
To upgrade the firewall performance and to have better IT productivity, it is necessary to optimize the rule base. This firewall rule optimization can be done by performing the following tasks:
- Getting rid of the purpose-less occult rules.
- Disabling those objects and rules that have remained unused over time and now have expired.
- Prioritizing firewall rules regarding the performance and effectiveness of the system.
- Removing those connections and/or irrelevant routes that are not being used.
- Making use of object naming procedures.
- Assessing the VPN parameters for the location of those groups and users that are expired or not attached or not used.
- Setting up rules that permit the access of policy usage against the firewall logs.
- Searching up various rules that resemble or may seem similar and combining them to form one rule.
Inquire about matters pertaining to fundamental firewall policy maintenance:
- Do any uncommented regulations or regulations pertain to configurations in the cloud?
- How many regulations comprise the security policy of the firewall? What was the quantity at the time of the most recent audit? A year ago?
- Have any policy provisions been deactivated, encompassing virtual private networks or network environments?
- Are there any superfluous regulations that ought to be eliminated?
- Are there any standards that are excessively lenient, such as those that permit the inclusion of over 1,000 IP addresses in the source or destination? It is possible that you prefer a value less than 1,000. It is recommended to maintain it at approximately 25.)
- Are there any regulations that permit at-risk Internet services, such as those that compromise network security, to enter the system?
- Do any regulations contravene our organization's security policy, which includes SOX and PCI DSS?
- Are there any regulations that permit Internet traffic to reach sensitive databases, servers, networks, or devices?
- Are there any regulations that permit direct Internet traffic to the internal network, excluding the DMZ?
5. Assess Risk, Check Issues, Fix
It is important to ensure that the rules are made according to the internal policies and relevant regulatory standards of the network system. These rules are ensured when a detailed risk assessment is carried out to get rid of such risky rules which may not be complying with the network policies. It is thus very important to validate the following issues:
- Are the currently existing rules permitting risky services from the demilitarized zone(DMZ) to the internal network of the organization?
- Are the currently existing rules permitting risky services incoming from the internet?
- Are the currently existing rules permitting risky services outbound to the internet?
- Are there any optional rules present in any of the firewall user fields?
- Are the currently existing rules in any way affecting the security policy of the organization?
- Assign and document a remediation action plan for compliance exceptions and risks identified through risk analysis.
- Confirm that all remediation efforts and rule modifications have been executed accurately.
- Track and record the completion of remediation efforts.
6. Ongoing Audits
After performing a successful audit, it is important to ensure that all the next audits which will be carried out will comply with these rules by following a few more tips mentioned below:
- It is important to establish a repeatable process that helps in the regular conduction of audits.
- It is important to create an alerting process that may notify the organization whenever a rule is modified or whenever there may be a risky policy.
- There should be the implementation of automated analysis and reporting so that the error-prone manual tasks are able to be replaced.
- It is crucial to maintain comprehensive documentation of all audit procedures, which should detail every firewall management activity.
- Ensure a robust workflow for firewall change management is established to ensure long-term compliance.
How to Run an Audit on OPNsense?
As your trusted open-source security solution, OPNsense developers do care a great deal about security, and with their frequent release schedule, they attempt to prevent issues from occurring. However, even when they are careful and well-informed, problems might arise. Therefore, it is important to be prepared.
Even while OPNsense users are constantly urged to update often, this is not always practical for a variety of reasons. Fortunately, OPNsense's firmware module has an integrated security check for known vulnerabilities. In this instance, you have the option to assess the danger of continuing to use the current version for a little longer.
You may run an audit on your OPNsense firewall by following the steps below:
-
Navigate to the System > Firmware > Status.
-
Click on the Run an audit dropdown menu.
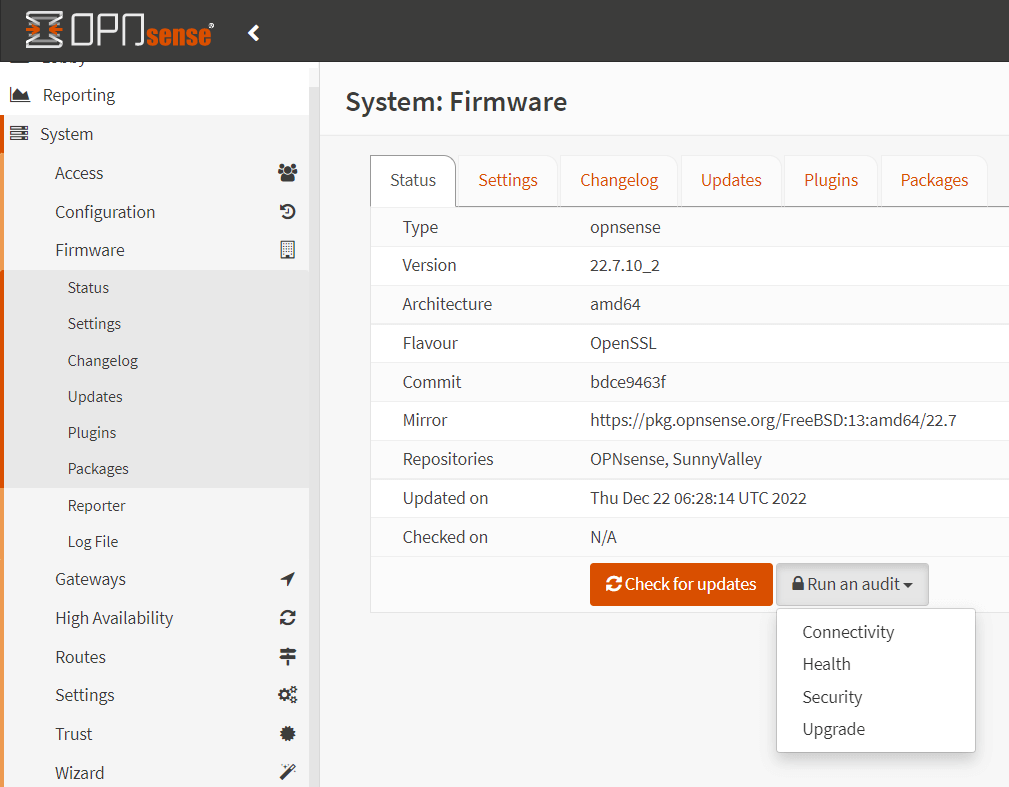 Figure 2. How to run an audit on OPNsense?
Figure 2. How to run an audit on OPNsense? -
You may click on the Connectivity option to see whether there are any connectivity issues between your node and the repository servers. If everything goes properly, the following report should be displayed:
***GOT REQUEST TO AUDIT CONNECTIVITY***
Currently running OPNsense 22.7.10_2 (amd64/OpenSSL) at Tue Jan 10 07:38:47 UTC 2023
Checking connectivity for host: pkg.opnsense.org -> 89.149.211.205
PING 89.149.211.205 (89.149.211.205): 1500 data bytes
1508 bytes from 89.149.211.205: icmp_seq=0 ttl=53 time=63.566 ms
1508 bytes from 89.149.211.205: icmp_seq=1 ttl=53 time=60.997 ms
1508 bytes from 89.149.211.205: icmp_seq=2 ttl=53 time=62.237 ms
1508 bytes from 89.149.211.205: icmp_seq=3 ttl=53 time=90.637 ms
--- 89.149.211.205 ping statistics ---
4 packets transmitted, 4 packets received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 60.997/69.359/90.637/12.318 ms
Checking connectivity for repository (IPv4): https://pkg.opnsense.org/FreeBSD:13:amd64/22.7
Updating OPNsense repository catalogue...
Fetching meta.conf: . done
Fetching packagesite.pkg: .......... done
Processing entries: .......... done
OPNsense repository update completed. 820 packages processed.
Updating SunnyValley repository catalogue...
Fetching meta.conf: . done
Fetching packagesite.pkg: .. done
Processing entries: .... done
SunnyValley repository update completed. 31 packages processed.
All repositories are up to date.
Checking connectivity for host: pkg.opnsense.org -> 2001:1af8:4f00:a005:5::
ping: UDP connect: No route to host
Checking connectivity for repository (IPv6): https://pkg.opnsense.org/FreeBSD:13:amd64/22.7
Updating OPNsense repository catalogue...
pkg: https://pkg.opnsense.org/FreeBSD:13:amd64/22.7/latest/meta.txz: Non-recoverable resolver failure
repository OPNsense has no meta file, using default settings
pkg: https://pkg.opnsense.org/FreeBSD:13:amd64/22.7/latest/packagesite.pkg: Non-recoverable resolver failure
pkg: https://pkg.opnsense.org/FreeBSD:13:amd64/22.7/latest/packagesite.txz: Non-recoverable resolver failure
Unable to update repository OPNsense
Updating SunnyValley repository catalogue...
pkg: https://updates.sunnyvalley.io/opnsense/FreeBSD:13:amd64/22.7/OpenSSL/latest/meta.txz: Non-recoverable resolver failure
repository SunnyValley has no meta file, using default settings
pkg: https://updates.sunnyvalley.io/opnsense/FreeBSD:13:amd64/22.7/OpenSSL/latest/packagesite.pkg: Non-recoverable resolver failure
pkg: https://updates.sunnyvalley.io/opnsense/FreeBSD:13:amd64/22.7/OpenSSL/latest/packagesite.txz: Non-recoverable resolver failure
Unable to update repository SunnyValley
Error updating repositories!
***DONE***
4.You may click on the Health option to check the status of the installed packages and plugins. The following checks are performed during the Health Audit:
- Check installed kernel version
- Check installed kernel version
- Check installed base version
- Check for missing or altered base files
- Check installed repositories
- Check installed plugins
- Check locked packages
- Check for missing package dependencies
- Check for missing or altered package files
- Check for core packages consistency You should see a report similar to the one given below:
***GOT REQUEST TO AUDIT HEALTH***
Currently running OPNsense 22.7.10_2 (amd64/OpenSSL) at Tue Jan 10 07:40:50 UTC 2023
>>> Check installed kernel version
Version 22.7.9 is correct.
>>>Check installed kernel version
No problems detected.
>>> Check installed base version
Version 22.7.9 is correct.
>>> Check for missing or altered base files
Error 2 ocurred.
etc/sysctl.conf:
size (311, 345)
sha256digest (0x8c57d647047d84b9be4cddbb0b6d58c1d5839f148b62d1137b8bf2611f681cfd, 0x06ec8255e5fdfb4ccaf2059bc0d12c92554e4ba8f92b9d4c51af74ba58ba00c9)
>>> Check installed repositories
SunnyValley
OPNsense
>>> Check installed plugins
os-intrusion-detection-content-snort-vrt 1.1_1
os-sensei 1.12.3
os-sensei-agent 1.12.3
os-sensei-updater 1.12
os-sunnyvalley 1.2_2
os-wireguard 1.13_3
>>> Check locked packages
No locks found.
>>> Check for missing package dependencies
Checking all packages: .......... done
>>> Check for missing or altered package files
Checking all packages: .......... done
>>> Check for core packages consistency
Core package "opnsense" has 63 dependencies to check.
Checking packages: ................................................................. done
***DONE***
When mismatches are indicated, you may reinstall impacted packages by navigating to System > Firmware > Packages.
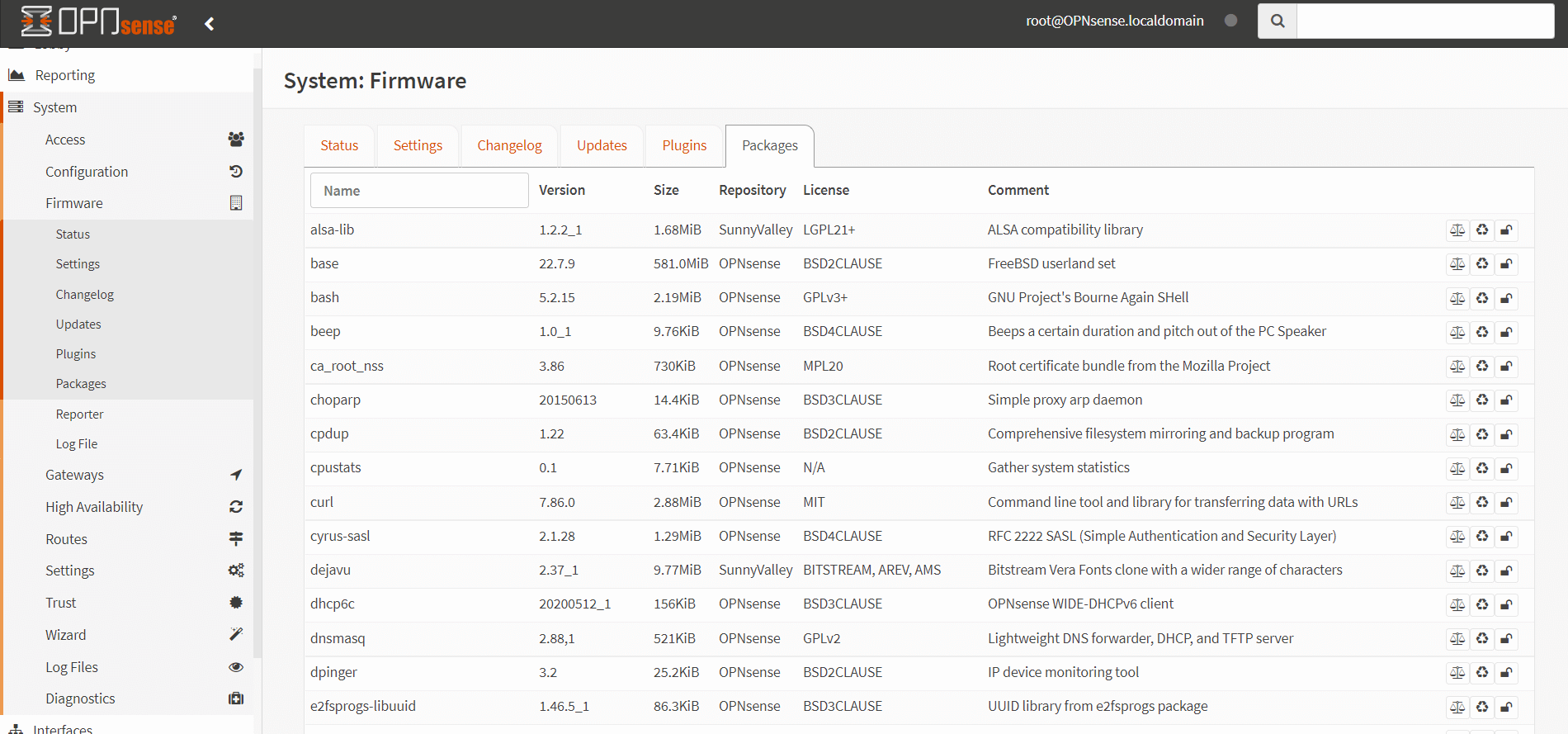
Figure 3. Installing broken packages on OPNsense
-
You may click on Security option to generate the security report. If everything goes properly, the following report should be displayed:
***GOT REQUEST TO AUDIT SECURITY***
Currently running OPNsense 22.7.10_2 (amd64/OpenSSL) at Tue Jan 10 07:23:43 UTC 2023
Fetching vuln.xml.xz: .......... done
0 problem(s) in 0 installed package(s) found.
***DONE*** -
To view the logs generated during the last OPNsense upgrade operation, click on the Upgrade option. You should see the upgrade log report similar to the given below:
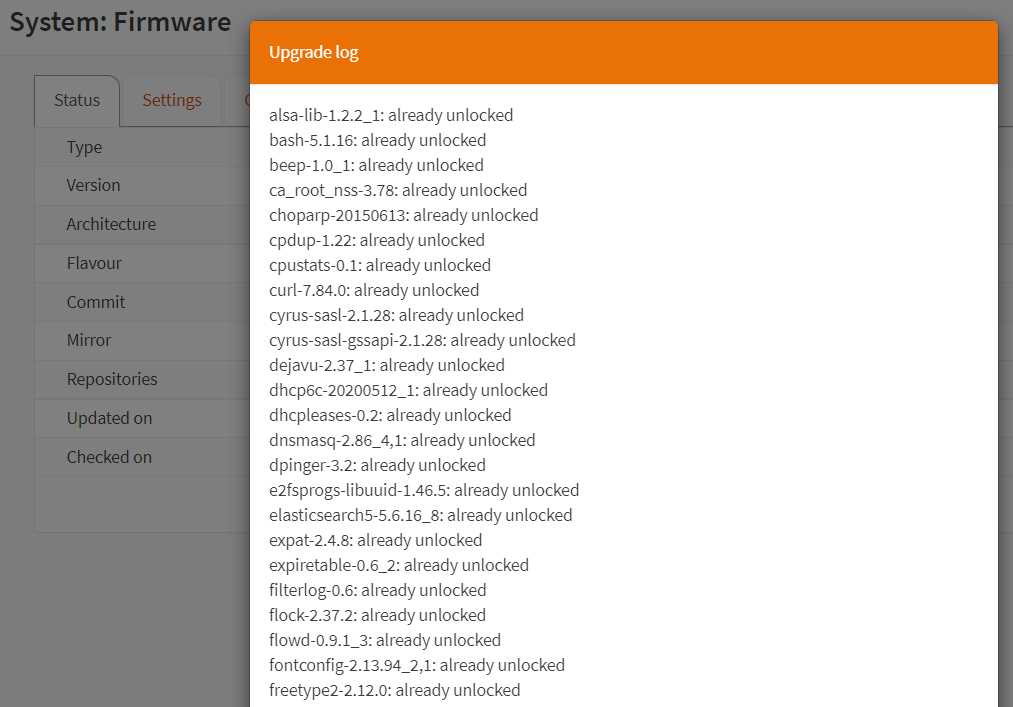
Figure 4. Viewing Upgrade logs on OPNsense
You may scroll down in the log window to view all logs. Click on the Clear button to remove the logs or click on the Close button to close the log window.
Hands on Video for Running Audit on OPNsense
You may watch the following video which shows how you can perform audit on an OPNsense firewall:
What is a Firewall Audit Tool?
A firewall auditing system is an important factor in the establishment of a network. It helps in maintaining the security of the network by preventing it from unauthorized traffic which may be malicious and dangerous to the network. Having an analysis of the firewall helps in remaining up-to-date with all the messages or transactions that are being made between the device and the network or even with an external network.
The firewall audit tools help in securing the network and enable the organization to invalidate the configuration so that the auditors are pleased that the organization follows the described policies, passes the standard checklist, makes the authorized changes, and that the intended access is granted. The firewall compliance tools enable the network to improve its performance and security, reduce downtime and of course help the authorized personnel to address the firewall issues and analyze the configurations.
Firewall audit tools help in meeting the business efficiencies and security of the system. These tools are used for scrutinizing internal, public, or other regulatory audits. There are more than a hundred rules the firewall systems have to follow which increases the chances of errors and misconfigurations. Thus the firewall management software is used in order to help with the optimization of rules and management of the firewall changes.
The firewall setup is an error-prone task. These configuration errors bring up the security issues which are faced by the network system or organization. The firewall audit tools come in handy when firewall management seems like too much struggle. Following are some of the firewall management solutions and firewall audit tools that help in the maintenance of firewall systems:
- Skybox
- SolarWinds
- Nippers
- FireMon
- ManageEngine Firewall Analyzer
- AlgoSec
- Tufin
1. Skybox
The Skybox Security Suite is software that integrates the data from firewalls and other networks that seem vulnerable so that the security issues may be prioritized. Skybox helps in the optimization of rules with the assurity that new changes will not bring any risk to the network.
It helps in keeping the network bound within the described policies and reduces the risks presented to firewalls. It deals with global vendors and helps in the compliance of risk identification, security maintenance, optimization of firewall systems, simplified auditing and reporting, and much more than just this.
2. SolarWinds
SolarWinds' Network Firewall Security Management software is designed for monitoring multi-vendor firewalls. It provides the recent firewall activity and helps in the identification of anonymous potential threats to the network system. It ensures that only the authorized firewall personnel are allowed to make changes in the firewall system.
SolarWinds' software provides a set of authorized rules which can be used as they are or altered according to the network policies or can even be created on your own. According to your set of rules, Solarwinds helps in receiving real-time information about the malware, anonymous potential threats to the network. For the determination of the firewall audit trail, a time window can be selected to run a specific program and then be provided with the details of that particular user.
3. Nippers
Nipper auditing tool helps in identifying the vulnerabilities in the firewall system or routers that may appear as potential threats or risks to the network. This auditing tool helps in the reduction of false positives within the network system which easily leads us to the actual vulnerabilities of the network allowing us to prioritize the current risks, perform analysis of our resources and prioritize the solution to fix the problems.
This ability of the system to identify the actual vulnerabilities along with a few false positives and the automatic risk prioritization makes it flexible, easily configurable and provides us with easy-to-read reports.
4. FireMon
The FireMon security managing tool is excellent for enterprise networks. It helps in the optimization of network configuration which makes it easier for the network administrators to analyze and regulate the security.
FireMon comes as a solution for the three main challenges faced by the firewall; compatibility, clean up and replacement, FireMon helps in verifying the policies for administrative changes and notifies whenever network access is changed. The most noticeable function of FireMon is its ability to analyze traffic flow. FireMon normalizes the policies across firewalls and other devices so that the scale of heterogeneous requirements is met.
5. ManageEngine Firewall Analyzer
This system caters the businesses in-house or especially in the industries. ManageEngine Firewall Analyzer plays a role in the management of network, visualization of data, blogs, events, compliance reporting, and similar. The usage of firewall rules can be analyzed and they can be optimized for better performance.
If at any time the changes are made in the network, you are instantly notified about all the changes made. Also, the IP addresses, VPNs, and bandwidth spikes can be monitored which makes the analysis of users easier and more accurate.
6. AlgoSec
AlgoSec is a worldwide network security system that has the main focus regarding businesses. It provides an in-depth analysis of the network system's policies and hence makes these policies optimizable. Most organizations have multiple firewalls from different vendors which means if you need to change a certain policy you need to log in to individual firewalls and make the respective changes. But with AlgoSec you can just set the renewed policies for all the vendors through a single administration panel. Thus AlgoSec turns out to be suitable for optimizing firewall security, change management, and even application discovery.
7. Tufin
Tufin is a network security program that enables organizations to automate the security policies, get a hang of the risk management, and is helpful in hybrid, multi-vendor environments. Tufin helps in enabling business connectivity through optimizing security policies.
A centrally unified security policy is established which helps in allowing or blocking the traffic flow and this centrally unified security policy can be applied across a hybrid network. This central security helps in identifying policy violations and risky accesses and keeps the organization up to date to maintain the strength of the security of the organization.