How to Install Apache, MySQL, PHP and PHPMyAdmin on FreeBSD?
FreeBSD (operating system), Apache (webserver), MySQL (database server), and PHP (to process dynamic PHP content) make up the FAMP acronym. A FAMP stack, comparable to a LAMP stack on Linux, is a collection of open-source software that, when installed collectively, enables a FreeBSD server to host dynamic web pages and web applications.
In this tutorial, we will guide you to install a FAMP stack on a FreeBSD 13.1 server using pkg, FreeBSD package manager. We will also cover the phpMyAdmin installation on FreeBSD server.
Installing FAMP Stack on FreeBSD?
You may easily install FAMP stack on your FreeBSD server by following the 6 main steps explained below:
-
Install Apache Webserver
-
Install MySQL Database server
-
Install PHP
-
Install PHP Modules (Optional)
-
Configure Apache
-
Verify PHP
What are the Prerequisites?
Before beginning this tutorial, you must have the following:
-
FreeBSD 13.1 server
-
Access to a user with root rights (or the ability to utilize sudo) In order to perform configuration modifications
-
Ensure that ports
80and443are accessible as part of your configuration.
Moreover, It is preferable to ensure that our system is up to date by running the next command:
pkg update && pkg upgrade -y
This will update your system and you may see an output similar to the given below:
Updating FreeBSD repository catalogue...
FreeBSD repository is up to date.
All repositories are up to date.
Updating FreeBSD repository catalogue...
FreeBSD repository is up to date.
All repositories are up to date.
Checking for upgrades (46 candidates): 100%
Processing candidates (46 candidates): 100%
The following 18 package(s) will be affected (of 0 checked):
Installed packages to be UPGRADED:
ca_root_nss: 3.83 -> 3.86
curl: 7.85.0 -> 7.87.0
expat: 2.4.9 -> 2.5.0
.........
readline: 8.1.2 -> 8.2.0
ruby30-gems: 3.3.23 -> 3.3.26
Number of packages to be upgraded: 18
28 MiB to be downloaded.
[1/18] Fetching p5-IO-Socket-SSL-2.077.pkg: 100% 180 KiB 183.8kB/s 00:01
.........
[18/18] Fetching ca_root_nss-3.86.pkg: 100% 266 KiB 272.8kB/s 00:01
Checking integrity... done (0 conflicting)
[1/18] Upgrading p5-URI from 5.12 to 5.17...
[1/18] Extracting p5-URI-5.17: 100%
.........
[17/18] Upgrading git from 2.38.1_1 to 2.39.0...
===> Creating groups.
Using existing group 'git_daemon'.
===> Creating users
Using existing user 'git_daemon'.
[17/18] Extracting git-2.39.0: 100%
[18/18] Upgrading nano from 6.4 to 7.1...
[18/18] Extracting nano-7.1: 100%
1. How to Install Apache Webserver?
Apache is now the most common web server in the world, making it an excellent option for hosting a website. Apache may be installed using pkg, FreeBSD's package manager. To install and start the Apache webserver on your FreeBSD node, you may follow the next steps given below:
-
To install Apache 2.4 package, run the following command:
pkg install apache24tipYou may use the following command to find the current apache package available in the repository:
pkg search apache -
Type
yto confirm the installation of Apache and its dependencies.Updating FreeBSD repository catalogue...
FreeBSD repository is up to date.
All repositories are up to date.
The following 5 package(s) will be affected (of 0 checked):
New packages to be INSTALLED:
apache24: 2.4.54
apr: 1.7.0.1.6.1_2
gdbm: 1.23
jansson: 2.14
libxml2: 2.10.3_1
Number of packages to be installed: 5
The process will require 38 MiB more space.
7 MiB to be downloaded.
Proceed with this action? [y/N]:
[1/5] Fetching jansson-2.14.pkg: 100% 46 KiB 47.5kB/s 00:01
[2/5] Fetching libxml2-2.10.3_1.pkg: 100% 1 MiB 1.2MB/s 00:01
[3/5] Fetching apr-1.7.0.1.6.1_2.pkg: 100% 467 KiB 478.1kB/s 00:01
[4/5] Fetching apache24-2.4.54.pkg: 100% 5 MiB 1.8MB/s 00:03
[5/5] Fetching gdbm-1.23.pkg: 100% 209 KiB 213.8kB/s 00:01
Checking integrity... done (0 conflicting)
[1/5] Installing gdbm-1.23...
[1/5] Extracting gdbm-1.23: 100%
[2/5] Installing jansson-2.14...
[2/5] Extracting jansson-2.14: 100%
[3/5] Installing libxml2-2.10.3_1...
[3/5] Extracting libxml2-2.10.3_1: 100%
[4/5] Installing apr-1.7.0.1.6.1_2...
[4/5] Extracting apr-1.7.0.1.6.1_2: 100%
[5/5] Installing apache24-2.4.54...
===> Creating groups.
Using existing group 'www'.
===> Creating users
Using existing user 'www'.
[5/5] Extracting apache24-2.4.54: 100%
=====
Message from apr-1.7.0.1.6.1_2:
--
The Apache Portable Runtime project removed support for FreeTDS with version 1.6. Users requiring MS-SQL connectivity must migrate
configurations to use the added ODBC driver and FreeTDS' ODBC features.
=====
Message from apache24-2.4.54:
--
To run apache www server from startup, add apache24_enable="yes"
in your /etc/rc.conf. Extra options can be found in startup script.
Your hostname must be resolvable using at least 1 mechanism in
/etc/nsswitch.conf typically DNS or /etc/hosts or apache might
have issues starting depending on the modules you are using.
- apache24 default build changed from static MPM to modular MPM
- more modules are now enabled per default in the port
- icons and error pages moved from WWWDIR to DATADIR
If build with modular MPM and no MPM is activated in
httpd.conf, then mpm_prefork will be activated as default
MPM in etc/apache24/modules.d to keep compatibility with
existing php/perl/python modules!
Please compare the existing httpd.conf with httpd.conf.sample
and merge missing modules/instructions into httpd.conf! -
To enable Apache to run as a service at boot, you must add
apache24_enable="YES"line to the /etc/rc.conf file by running the next command:sysrc apache24_enable="YES" -
To start the apache web service, run the following command:
service apache24 start -
To verify that apache server is running, run the next command:
service apache24 status
You should see the output similar to the below:
apache24 is running as pid 4128.
You may connect the webserver by typing http://your_server_IP_address/ on your web browser. You should see the default Apache web page for FreeBSD. It Works! will appear, indicating that your web server has been successfully deployed.
2. How to Install MySQL?
Now that your web server is operational. You may install MySQL that is is an open source and free relational database management system on your FreeBSD server. It maintains tabular data storage. The MySQL server will arrange and offer access to databases that your server may use to store data. It is the most common method for storing data in a database.
-
To install MySQL 8.0 package, run the following command:
pkg install mysql80-servertipYou may use the following command to find the current
mysqlpackage available in the repository:pkg search mysql -
Type
yto confirm the installation of MySQL and its dependencies.Updating FreeBSD repository catalogue...
FreeBSD repository is up to date.
All repositories are up to date.
The following 17 package(s) will be affected (of 0 checked):
New packages to be INSTALLED:
cyrus-sasl: 2.1.28
groff: 1.22.4_4
hidapi: 0.12.0
icu: 72.1,1
libcbor: 0.9.0
libcjson: 1.7.15
libevent: 2.1.12
libfido2: 1.12.0
liblz4: 1.9.4,1
libpaper: 1.1.28
mysql80-client: 8.0.31
mysql80-server: 8.0.31
openldap26-client: 2.6.3
protobuf: 3.21.9,1
psutils: 1.17_5
uchardet: 0.0.8
zstd: 1.5.2_1
Number of packages to be installed: 17
The process will require 412 MiB more space.
42 MiB to be downloaded.
Proceed with this action? [y/N]:
[1/17] Fetching libcjson-1.7.15.pkg: 100% 35 KiB 35.7kB/s 00:01
[2/17] Fetching liblz4-1.9.4,1.pkg: 100% 144 KiB 147.9kB/s 00:01
[3/17] Fetching groff-1.22.4_4.pkg: 100% 3 MiB 2.9MB/s 00:01
[4/17] Fetching hidapi-0.12.0.pkg: 100% 32 KiB 33.1kB/s 00:01
[5/17] Fetching mysql80-server-8.0.31.pkg: 100% 18 MiB 2.8MB/s 00:07
[6/17] Fetching zstd-1.5.2_1.pkg: 100% 589 KiB 603.5kB/s 00:01
[7/17] Fetching mysql80-client-8.0.31.pkg: 100% 3 MiB 3.6MB/s 00:01
[8/17] Fetching libcbor-0.9.0.pkg: 100% 30 KiB 30.4kB/s 00:01
[9/17] Fetching uchardet-0.0.8.pkg: 100% 112 KiB 114.3kB/s 00:01
[10/17] Fetching cyrus-sasl-2.1.28.pkg: 100% 967 KiB 989.9kB/s 00:01
[11/17] Fetching icu-72.1,1.pkg: 100% 11 MiB 2.9MB/s 00:04
[12/17] Fetching psutils-1.17_5.pkg: 100% 59 KiB 59.9kB/s 00:01
[13/17] Fetching libpaper-1.1.28.pkg: 100% 24 KiB 24.4kB/s 00:01
[14/17] Fetching openldap26-client-2.6.3.pkg: 100% 1 MiB 1.1MB/s 00:01
[15/17] Fetching protobuf-3.21.9,1.pkg: 100% 3 MiB 1.6MB/s 00:02
[16/17] Fetching libfido2-1.12.0.pkg: 100% 234 KiB 239.3kB/s 00:01
[17/17] Fetching libevent-2.1.12.pkg: 100% 322 KiB 330.0kB/s 00:01
Checking integrity... done (0 conflicting)
[1/17] Installing libcjson-1.7.15...
[1/17] Extracting libcjson-1.7.15: 100%
[2/17] Installing libpaper-1.1.28...
[2/17] Extracting libpaper-1.1.28: 100%
[3/17] Installing liblz4-1.9.4,1...
[3/17] Extracting liblz4-1.9.4,1: 100%
[4/17] Installing libcbor-0.9.0...
[4/17] Extracting libcbor-0.9.0: 100%
[5/17] Installing uchardet-0.0.8...
[5/17] Extracting uchardet-0.0.8: 100%
[6/17] Installing cyrus-sasl-2.1.28...
*** Added group `cyrus' (id 60)
*** Added user `cyrus' (id 60)
[6/17] Extracting cyrus-sasl-2.1.28: 100%
[7/17] Installing psutils-1.17_5...
[7/17] Extracting psutils-1.17_5: 100%
[8/17] Installing groff-1.22.4_4...
[8/17] Extracting groff-1.22.4_4: 100%
[9/17] Installing hidapi-0.12.0...
[9/17] Extracting hidapi-0.12.0: 100%
[10/17] Installing zstd-1.5.2_1...
[10/17] Extracting zstd-1.5.2_1: 100%
[11/17] Installing icu-72.1,1...
[11/17] Extracting icu-72.1,1: 100%
[12/17] Installing openldap26-client-2.6.3...
[12/17] Extracting openldap26-client-2.6.3: 100%
[13/17] Installing protobuf-3.21.9,1...
[13/17] Extracting protobuf-3.21.9,1: 100%
[14/17] Installing libfido2-1.12.0...
[14/17] Extracting libfido2-1.12.0: 100%
[15/17] Installing libevent-2.1.12...
[15/17] Extracting libevent-2.1.12: 100%
[16/17] Installing mysql80-client-8.0.31...
[16/17] Extracting mysql80-client-8.0.31: 100%
[17/17] Installing mysql80-server-8.0.31...
===> Creating groups.
Creating group 'mysql' with gid '88'.
===> Creating users
Creating user 'mysql' with uid '88'.
===> Creating homedir(s)
[17/17] Extracting mysql80-server-8.0.31: 100%
=====
Message from cyrus-sasl-2.1.28:
--
You can use sasldb2 for authentication, to add users use:
saslpasswd2 -c username
If you want to enable SMTP AUTH with the system Sendmail, read
Sendmail.README
NOTE: This port has been compiled with a default pwcheck_method of
auxprop. If you want to authenticate your user by /etc/passwd,
PAM or LDAP, install ports/security/cyrus-sasl2-saslauthd and
set sasl_pwcheck_method to saslauthd after installing the
Cyrus-IMAPd 2.X port. You should also check the
`/usr/local/lib/sasl2/*.conf` files for the correct
pwcheck_method.
If you want to use GSSAPI mechanism, install
ports/security/cyrus-sasl2-gssapi.
If you want to use SRP mechanism, install
ports/security/cyrus-sasl2-srp.
If you want to use LDAP auxprop plugin, install
ports/security/cyrus-sasl2-ldapdb.
=====
Message from groff-1.22.4_4:
--
In order to be able to use the html driver, you need to install the following packages:
- ghostscript
- netpbm
=====
Message from openldap26-client-2.6.3:
--
The OpenLDAP client package has been successfully installed.
Edit /usr/local/etc/openldap/ldap.conf
to change the system-wide client defaults.
Try `man ldap.conf` and visit the OpenLDAP FAQ-O-Matic at
http://www.OpenLDAP.org/faq/index.cgi?file=3
for more information.
=====
Message from mysql80-client-8.0.31:
-
This is the mysql CLIENT without the server.
for complete server and client, please install databases/mysql80-server
=====
Message from mysql80-server-8.0.31:
--
There is no initial password for first time use of MySQL.
Keep in mind to reset it to a secure password.
MySQL80 has a default /usr/local/etc/mysql/my.cnf,
remember to replace it with your own
or set `mysql_optfile="$YOUR_CNF_FILE` in rc.conf. -
To enable MySQL to run as a service at boot, you must add
mysql_enable="YES"line to the /etc/rc.conf file by running the next command:sysrc mysql_enable="YES" -
To start the MySQL service, run the following command:
service mysql-server start -
To verify that MySQL server is running, run the next command:
service mysql-server statusYou should see the output similar to the below:
mysql is running as pid 6816. -
Now that your MySQL database is up and running, you will need to execute a simple security script to remove certain potentially harmful defaults and modestly limit access to your database system.
You may run the following command to enhance the security of your database by launching the interactive mysql security script:
mysql_secure_installation
The script will request that you establish a password. Since you just installed MySQL, it is probable that you do not have one; thus, enter Y and continue with the steps. You may press 2 to set a strong password.
At each prompt for the remaining questions, you must press the y key to accept the suggested safe values. This will delete some example users and databases, deactivate remote root logins, and load these new rules so that MySQL respects your modifications instantly.
Your database system is now configured, and you can proceed to installing PHP.
Securing the MySQL server deployment.
Connecting to MySQL using a blank password.
VALIDATE PASSWORD COMPONENT can be used to test passwords
and improve security. It checks the strength of password
and allows the users to set only those passwords which are
secure enough. Would you like to setup VALIDATE PASSWORD component?
Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No: y
There are three levels of password validation policy:
LOW Length >= 8
MEDIUM Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, and special characters
STRONG Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, special characters and dictionary file
Please enter 0 = LOW, 1 = MEDIUM and 2 = STRONG: 2
Please set the password for root here.
New password:
Re-enter new password:
Estimated strength of the password: 100
Do you wish to continue with the password provided?(Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
By default, a MySQL installation has an anonymous user,
allowing anyone to log into MySQL without having to have
a user account created for them. This is intended only for
testing, and to make the installation go a bit smoother.
You should remove them before moving into a production
environment.
Remove anonymous users? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
Success.
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from
'localhost'. This ensures that someone cannot guess at
the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
Success.
By default, MySQL comes with a database named 'test' that
anyone can access. This is also intended only for testing,
and should be removed before moving into a production
environment.
Remove test database and access to it? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
- Dropping test database...
Success.
- Removing privileges on test database...
Success.
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes
made so far will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
Success.
All done!
How to Configure MySQL Database?
You may customize your MySQL database configuration by following the samples given below.
-
To connect your MySQL database CLI interface as
root, you may run the following command:mysql -u root -pAfter entering the MySQL root password you may run queries as you wish.
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 8
Server version: 8.0.31 Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2022, Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
root@localhost [(none)]> -
Change the username of the root user to something a little more random and flush the currently loaded privileges for the change to take effect, run the next command:
UPDATE mysql.user set user = '[username]' where user = 'root';
flush privileges;Do not forget to exit the MySQL CLI (exit) and log in with the new username (reentering the password when requested) to check the change was successful:
mysql -u [username] -p -
MySQL does not generate a custom configuration file (
.cnf) by default, but it does contain a default configuration file that should not be modified directly. To create a configurable MySQL configuration file, transfermy-default.cnfto/var/db/mysql/my.cnf, run the next command:sudo cp /usr/local/share/mysql/my-default.cnf /var/db/mysql/my.cnf -
You may use the following MySQL command to see the currently loaded MySQL variables (will need to perform in terminal with the command above to enter mode, or maybe a MySQL tool such as Sequel Pro) (use
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE '%variable name%'to display a particular loaded variable):SHOW VARIABLES -
Using the following command, update the MySQL configuration file, and then delete the warning at the start of the file against altering this file:
sudo ee /var/db/mysql/my.cnf -
Uncomment and update the
innodb_buffer_pool_sizeto the desired size (notice the MySQL comment that advises setting it to 70% of the total server RAM if the machine is utilized as a dedicated server). i.e. 512mb / 100 * 70 = ~358mb)innodb_buffer_pool_size = 358M -
Add the max connections directive with a required value to set the maximum number of concurrent MySQL requests (note that max_connections is max_connections + 1 for administrative use). Note that there is no straightforward method for calculating this; MySQL states that it "depends on the quality of the thread library on a specific platform, the amount of RAM available, the amount of RAM consumed by each connection, the workload from each connection, and the required response time":
max_connections = 501 -
Add the
query_cache_sizedirective and set it to0to deactivate the query cache size restriction, or a very tiny number (Caution: setting this to a value that is too high might slow down the system. Comparative analysis and investigation will be required):query cache size = 0
3. How to Install PHP?
PHP is the component of your system that processes and displays code for dynamic content. Without PHP, the dynamic websites you want to deploy on your server will not function properly. It is able to execute scripts, connect to MySQL databases to get data and pass the output to the web server for display.
You may once again install your components via the pkg system. Additionally, you will include mod_php, php-mysql, and php-mysqli.
-
To install PHP 8.2 using
pkg, use the following command:pkg install php82 php82-mysqli mod_php82tipYou may use the following command to find the current
PHPpackage available in the repository:pkg search php -
Type
yto confirm the installation of PHP and its dependencies.This installs the php82, php82-mysqli, and mod_php82 packages.Updating FreeBSD repository catalogue...
FreeBSD repository is up to date.
All repositories are up to date.
The following 4 package(s) will be affected (of 0 checked):
New packages to be INSTALLED:
libargon2: 20190702
mod_php82: 8.2.0
php82: 8.2.0
php82-mysqli: 8.2.0
Number of packages to be installed: 4
The process will require 35 MiB more space.
6 MiB to be downloaded.
Proceed with this action? [y/N]: y
[1/4] Fetching php82-mysqli-8.2.0.pkg: 100% 49 KiB 50.2kB/s 00:01
[2/4] Fetching php82-8.2.0.pkg: 100% 5 MiB 2.4MB/s 00:02
[3/4] Fetching mod_php82-8.2.0.pkg: 100% 2 MiB 1.8MB/s 00:01
[4/4] Fetching libargon2-20190702.pkg: 100% 63 KiB 64.3kB/s 00:01
Checking integrity... done (0 conflicting)
[1/4] Installing libargon2-20190702...
[1/4] Extracting libargon2-20190702: 100%
[2/4] Installing php82-8.2.0...
[2/4] Extracting php82-8.2.0: 100%
[3/4] Installing php82-mysqli-8.2.0...
[3/4] Extracting php82-mysqli-8.2.0: 100%
[4/4] Installing mod_php82-8.2.0...
[4/4] Extracting mod_php82-8.2.0: 100%
[activating module `php' in /usr/local/etc/apache24/httpd.conf]
=====
Message from php82-mysqli-8.2.0:
--
This file has been added to automatically load the installed extension:
/usr/local/etc/php/ext-20-mysqli.ini
=====
Message from mod_php82-8.2.0:
--
******************************************************************************
Make sure index.php is part of your DirectoryIndex.
You should add the following to your Apache configuration file:
<FilesMatch "\.php$">
SetHandler application/x-httpd-php
</FilesMatch>
<FilesMatch "\.phps$">
SetHandler application/x-httpd-php-source
</FilesMatch>
******************************************************************************
If you are building PHP-based ports in poudriere(8) or Synth with ZTS enabled,
add WITH_MPM=event to /etc/make.conf to prevent build failures.
****************************************************************************** -
Copy the example PHP configuration file to the specified location by running the next command:
cp /usr/local/etc/php.ini-production /usr/local/etc/php.ini -
To recreate the cached information on installed executable files run the following command:
rehash -
To enable and run the
php, you may execute the following commands:sysrc php_fpm_enable=yes
service php-fpm start -
To verify that PHP is running, execute the next command:
service php-fpm statusYou should see the output similar to the following one:
php_fpm is running as pid 6357.
You must configure PHP to operate with Apache before using it.
4. How to Install PHP Modules?
This step is optional and you may enhance the functionality of PHP by installing some PHP modules on your FreeBSD system. You may follow the next steps to install PHP modules:
-
To view the available PHP modules, run the next command:
pkg search php82You should see the output similar to the given below:
ZendFramework-php82-2.4.13 Framework for developing PHP web applications
adodb5-php82-5.22.4 Database library for PHP
ampache-php82-5.0.0 Web-based Audio file manager
arcanist-lib-php82-20220518_2 Libraries for the command line interface for Phabricator
arcanist-php82-20220518_2 Command line interface for Phabricator
aws-sdk-php82-3.232.3 PHP interface for Amazon Web Services (AWS)
bacula-web-php82-8.6.3_2 Bacula-web provides a summarized output of Bacula jobs
davical-php82-1.1.10 Simple CalDAV server using a postgres backend
dokuwiki-php82-20220731a_1 Simple and easy to use wiki, no database required
drush-php82-8.4.11 Drupal command line and scripting interface
hiawatha-monitor-php82-1.6 Monitoring tool for the Hiawatha webserver
icinga-ipl-i18n-php82-0.2.0 Icinga PHP library
icinga-php-library-php82-0.10.0 Icinga PHP library
icinga-php-thirdparty-php82-0.11.0 Icinga PHP thirdparty
php82-8.2.0 PHP Scripting Language (8.2.X branch)
php82-Ice37-3.7.6 Modern alternative to object middleware such as CORBA/COM/DCOM/COM+
php82-aphpbreakdown-2.2.2 Code-Analyzer for PHP for Compatibility check-UP
php82-aphpunit-2.1 Testing framework for unit tests
php82-bcmath-8.2.0 The bcmath shared extension for php
php82-brotli-0.13.1 Brotli extension for PHP
php82-bsdconv-11.6.0 PHP wrapper for bsdconv
...........
phpMyAdmin-php82-4.9.10 Set of PHP-scripts to manage MySQL over the web
phpMyAdmin5-php82-5.2.0 Set of PHP-scripts to manage MySQL over the web
...........
suphp-php82-0.7.2_2 Securely execute PHP scripts under Apache
tcexam-php82-15.0.1 Open Source system for electronic exams
typo3-11-php82-11.5.21 Typo3 content management system
unit-php82-1.29.0_1 PHP module for NGINX Unit
vexim-php82-2.3_3 Web interface for managing virtual domains for exim
websvn-php82-2.8.1 Online Subversion repository browser
zenphoto-php82-1.5.9 Simpler web photo gallery -
To learn more about what each module performs, you may read the detailed description of the package by using the
-foption. For instance, to find out functionality of thephpMyAdmin5-php82-5.2.0, you may run the following command:pkg search -f phpMyAdmin5-php82-5.2.0In addition to a vast number of additional material, you will discover the following:
phpMyAdmin5-php82-5.2.0
Name : phpMyAdmin5-php82
Version : 5.2.0
Origin : databases/phpmyadmin5
Architecture : FreeBSD:13:*
Prefix : /usr/local
Repository : FreeBSD [pkg+http://pkg.FreeBSD.org/FreeBSD:13:amd64/quarterly]
Categories : www databases
Licenses : GPLv2
Maintainer : joneum@FreeBSD.org
WWW : https://www.phpmyadmin.net/
Comment : Set of PHP-scripts to manage MySQL over the web
Options :
------------------------------------
Description :
Currently phpMyAdmin can:
* browse and drop databases, tables, views, columns and indexes
* display multiple results sets through stored procedures or queries
* create, copy, drop, rename and alter databases, tables, columns
and indexes
* maintain server, databases and tables, with proposals on server
configuration
* execute, edit and bookmark any SQL-statement, even batch-queries
* load text files into tables
* create and read dumps of tables
* export data to various formats: CSV, XML, PDF, ISO/IEC 26300 -
OpenDocument Text and Spreadsheet, Microsoft Word 2000, and
LATEX formats
* import data and MySQL structures from OpenDocument spreadsheets,
as well as XML, CSV, and SQL files
* administer multiple servers
* manage MySQL users and privileges
* check referential integrity in MyISAM tables
* using Query-by-example (QBE), create complex queries
automatically connecting required tables
* create PDF graphics of your database layout
* search globally in a database or a subset of it
* transform stored data into any format using a set of predefined
functions, like displaying BLOB-data as image or download-link
* track changes on databases, tables and views
* support InnoDB tables and foreign keys
* support mysqli, the improved MySQL extension
* create, edit, call, export and drop stored procedures and
functions
* create, edit, export and drop events and triggers
* communicate in 62 different languages
WWW: https://www.phpmyadmin.net/ -
To install one of the PHP modules, you may use
pkg install <package name>command where<package name>is the name of the package that you wish to install. For example, to install thephpMyAdmin5-php82-5.2.0, you may run the following command and pressyto confirm the installation:pkg install phpMyAdmin5-php82-5.2.0You should see the following output:
Updating FreeBSD repository catalogue...
FreeBSD repository is up to date.
All repositories are up to date.
The following 25 package(s) will be affected (of 0 checked):
New packages to be INSTALLED:
brotli: 1.0.9,1
fontconfig: 2.14.0,1
freetype2: 2.12.1_2
........
[23/25] Fetching php82-iconv-8.2.0.pkg: 100% 19 KiB 19.0kB/s 00:01
[24/25] Fetching tiff-4.4.0_1.pkg: 100% 864 KiB 885.1kB/s 00:01
[25/25] Fetching php82-filter-8.2.0.pkg: 100% 22 KiB 22.7kB/s 00:01
Checking integrity... done (0 conflicting)
[1/25] Installing png-1.6.39...
[1/25] Extracting png-1.6.39: 100%
[2/25] Installing jpeg-turbo-2.1.4...
[2/25] Extracting jpeg-turbo-2.1.4: 100%
.....
[23/25] Extracting php82-iconv-8.2.0: 100%
[24/25] Installing php82-filter-8.2.0...
[24/25] Extracting php82-filter-8.2.0: 100%
[25/25] Installing phpMyAdmin5-php82-5.2.0...
..........
=====
Message from phpMyAdmin5-php82-5.2.0:
--
phpMyAdmin5-php82-5.2.0 has been installed into:
/usr/local/www/phpMyAdmin
Please edit config.inc.php to suit your needs.
To make phpMyAdmin available through your web site, I suggest
that you add something like the following to httpd.conf:
Alias /phpmyadmin/ "/usr/local/www/phpMyAdmin/"
<Directory "/usr/local/www/phpMyAdmin/">
Options None
AllowOverride Limit
Require local
Require host .example.com
</Directory>
SECURITY NOTE: phpMyAdmin is an administrative tool that has had several remote vulnerabilities discovered in the past, some allowing remote attackers to execute arbitrary code with the web server's user credential.
All known problems have been fixed, but the FreeBSD Security Team strongly advises that any instance be protected with an additional protection layer,
e.g. a different access control mechanism implemented by the web server
as shown in the example. Do consider enabling phpMyAdmin only when it is in use.
5. How to Configure Apache to Use PHP Module?
The Apache HTTP server includes a separate configuration directory for individual modules. You must create one of these configuration files to integrate Apache HTTP with PHP by following the next steps:
-
Edit the
/usr/local/etc/apache24/modules.d/001_mod-php.confwith your favorite editor likevi: -
Add the following lines into the configuration file and exit.
<IfModule dir_module>
DirectoryIndex index.php index.html
<FilesMatch "\.php$">
SetHandler application/x-httpd-php
</FilesMatch>
<FilesMatch "\.phps$">
SetHandler application/x-httpd-php-source
</FilesMatch>
</IfModule> -
Edit the
/usr/local/etc/apache24/httpd.confwith your favorite editor likevi: -
Add the following lines into the configuration file and exit.
<Directory "/usr/local/www/phpMyAdmin/">
Options None
AllowOverride Limit
Require all granted
</Directory> -
Modify the
DirectoryIndex index.htmlline by changing it to the given below:DirectoryIndex index.php index.html -
To verify the Apache web server configuration, run the next command:
apachectl configtestYou should see the output similar to the following:
Performing sanity check on apache24 configuration:
Syntax OK -
You must restart the service for them to take effect because configuration changes have been made to Apache. If not, Apache will continue to function with the previous settings. To restart the Apache web server, run the following command:
apachectl restart
6. How to Verify PHP?
Prior starting working with the FAMP stack, it is advisable to ensure that PHP is functioning properly. To ensure that your system is correctly setup for PHP, you may construct a simple PHP script.In our example, we will create a script called info.php. For Apache to locate the file and serve it properly, it must be stored in the DocumentRoot directory, which is where Apache searches for files when a user hits the web server. The location of DocumentRoot is defined in the Apache configuration file /usr/local/etc/apache24/httpd.conf. DocumentRoot is by default set to /usr/local/www/apache24/data. You may follow the next steps to verify your PHP installation:
-
You may create the
/usr/local/www/apache24/data/info.phpfile by using your favorite editor: -
Add the following line in the the php file and exit:
<?php phpinfo(); ?> -
To check if your web server can successfully display PHP-generated content, visit this website by typing
[http://your_server_IP/info.php](http://your_server_ip/info.php)in your web browser. You should see the following page: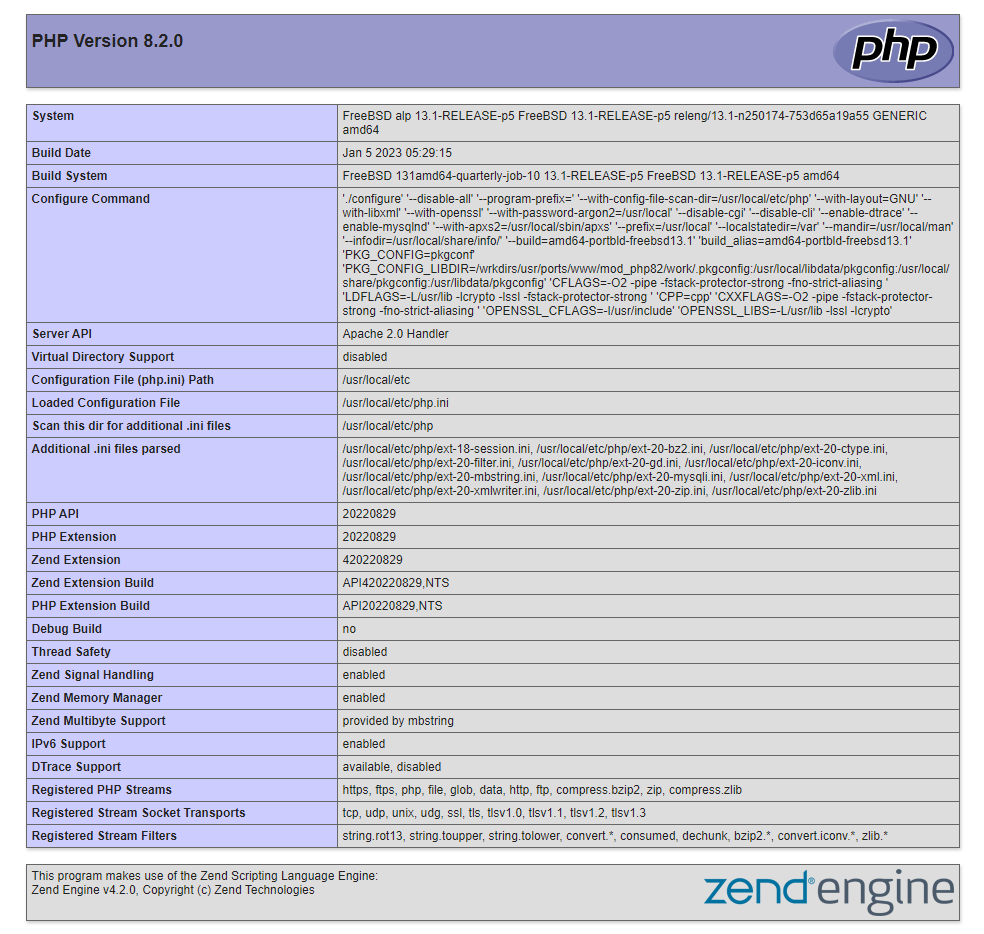
Figure 1. PHP info page
This page provides information on your server from a PHP viewpoint. It is helpful for troubleshooting and verifying that your settings are being successfully implemented. If this was successful, PHP is operating as intended.
tipThis file should be deleted after this test, since it might provide information about your server to unauthorized users. To do this, you may type:
rm /usr/local/www/apache24/data/info.phpYou may rebuild this page at any time if you need to view the information again in the future.
After installing a FAMP stack, you have several options for what to do next. You have installed a platform that allows you to install the vast majority of websites and web applications on your server.
How to Install phpMyAdmin?
phpMyAdmin is a free and open source tool used to administer a MySQL server instance through a graphical user interface. PHP is used to develop phpMyAdmin. This step is optional and to install phpMyAdmin utility you may follow these steps:
-
To install
wgettool, you may run the next command:pkg install wget -
Download phpMyAdmin from their Downloads page,
https://www.phpmyadmin.net/downloads/by running the following command. At the time this article was written, the most recent version is 5.2.0.wget https://files.phpmyadmin.net/phpMyAdmin/5.2.0/phpMyAdmin-5.2.0-all-languages.tar.gz -
Unzip the downloaded file by running the following command:
tar -xvf phpMyAdmin-5.2.0-all-languages.tar.gz -
Copy the extracted directory to
/usr/local/www/apache24/data/phpmyadminby running the next command:cp -r phpMyAdmin-5.2.0-all-languages /usr/local/www/apache24/data/phpmyadmin -
Copy the sample config file for phpMyAdmin by running the next command:
cd /usr/local/www/apache24/data/phpmyadmin/
cp config.sample.inc.php config.inc.php -
Uncomment the following line to the
/usr/local/etc/php.inifile for the installed extension.extension=mysqli.so -
Create a tmp directory for template caching and set its permissions by running the next commands:
mkdir /usr/local/www/apache24/data/phpmyadmin/tmp
chmod 777 /usr/local/www/apache24/data/phpmyadmin/tmp -
To activate the new settings, restart Apache by running the next command:
service apache24 restart -
You can now access phpMyAdmin UI via
http://your_server_IP/phpmyadmin.
Figure 2. phpMyAdmin Login Page
-
You may login using your MySQL DB root credentials.
tipIf you encounter a login problem by getting the following error notification
mysqli::real_connect(): The server requested authentication method unknown to the client [caching_sha2_password], it indicates that your MySQL server is utilizing thecaching_sha2_passwordauthentication technique. To resolve the issue, you must switch the authentication method to mysql_native_password as indicated below after starting the MySQL terminal interface withmysql -u root -pcommand.ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'Strong-Password';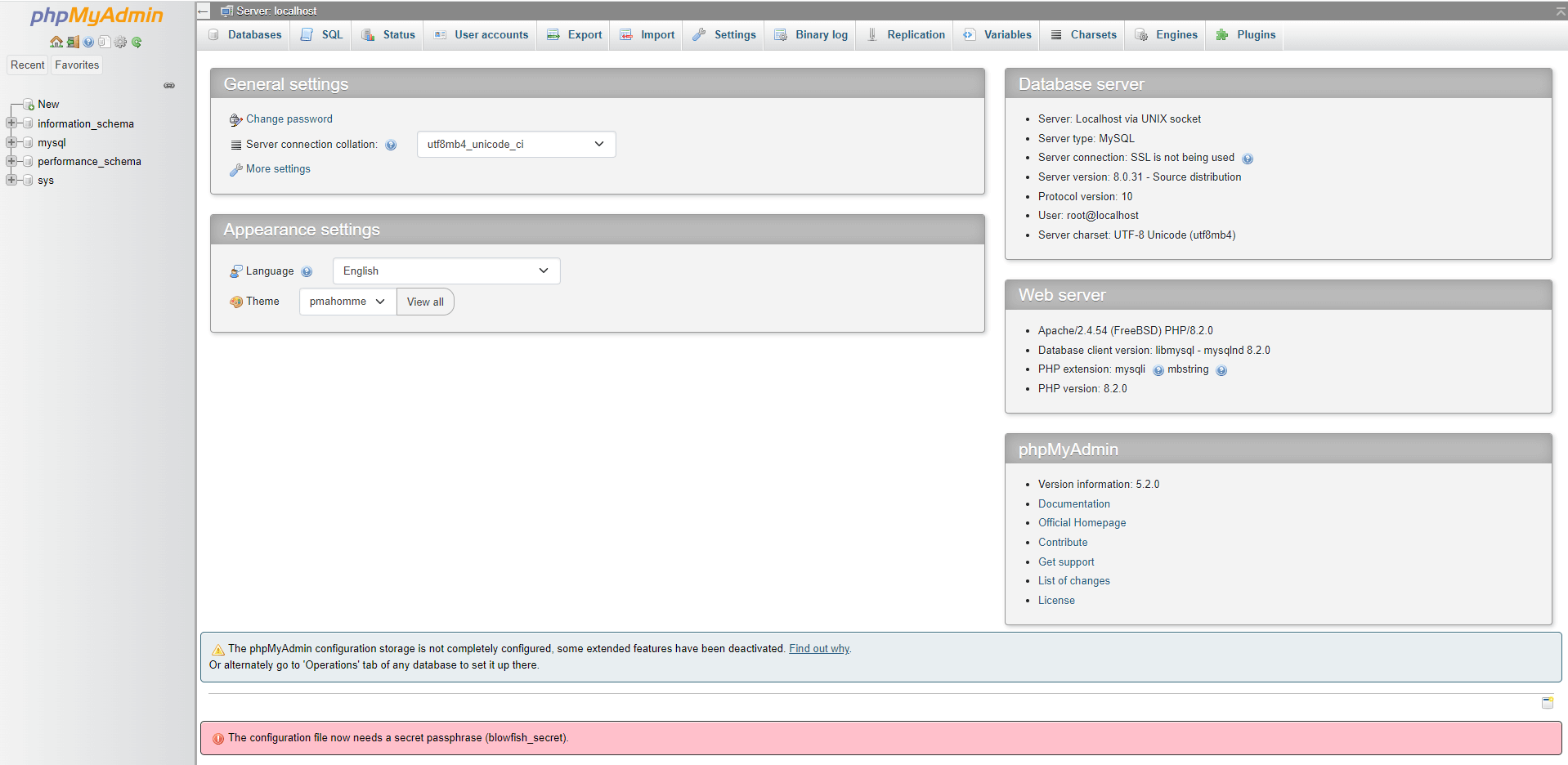
Figure 3. phpMyAdmin Settings Page
