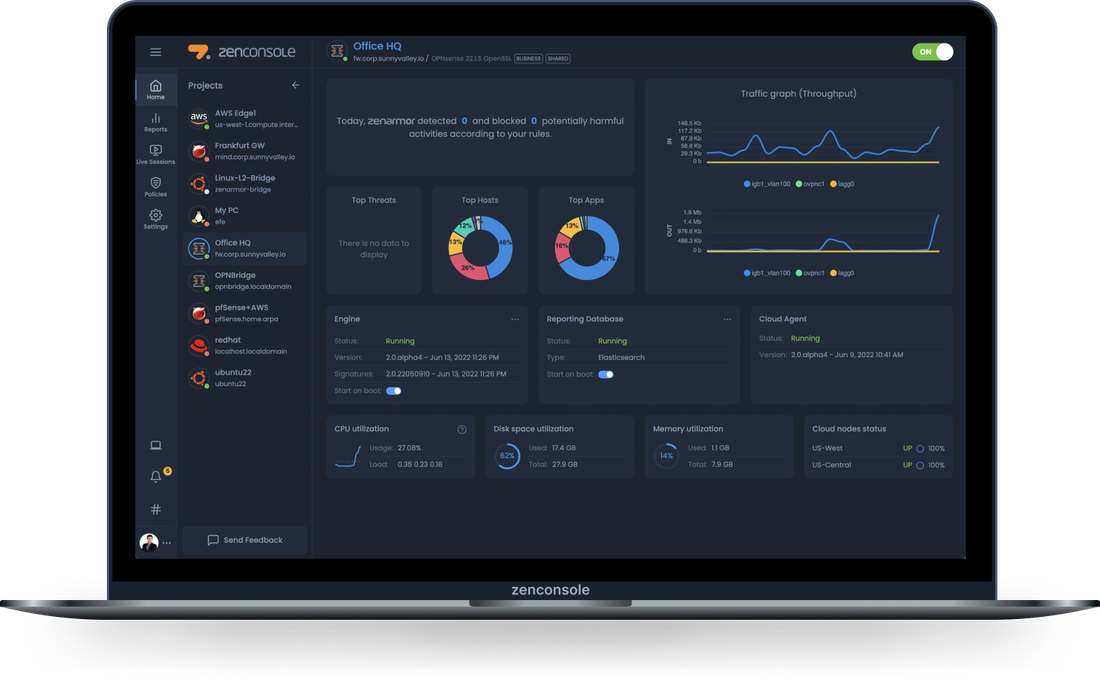
SASE (Secure Access Service Edge):
Focus: SASE primarily focuses on providing secure access to network resources, applications, and data for users, regardless of their location or the devices they use.
Key Features: SASE combines network security and wide-area networking (WAN) capabilities into a cloud-native service. It typically includes features like secure web gateways (SWG), firewall as a service (FWaaS), zero trust network access (ZTNA), and software-defined WAN (SD-WAN).
Use Cases: SASE is suitable for organizations looking to modernize their network and security infrastructure, especially for remote and mobile users. It offers a comprehensive approach to secure access and connectivity.
NGFW (Next-Generation Firewall):
Focus: NGFW is primarily focused on network security, particularly at the perimeter of an organization's network. It aims to protect against a wide range of threats, including malware, intrusions, and unauthorized access.
Key Features: NGFWs go beyond traditional firewalls by incorporating advanced security features such as application-layer filtering, intrusion prevention systems (IPS), SSL/TLS inspection, and more.
Use Cases: NGFWs are ideal for organizations that need robust network security, including protection against advanced threats and fine-grained control over network traffic. They are typically deployed at network entry and exit points.
SWG (Secure Web Gateway):
Focus: SWG primarily focuses on securing web traffic and content. It controls and filters web access, enforces security policies, and protects against web-based threats.
Key Features: SWGs offer features like URL filtering, content inspection, data loss prevention (DLP), malware protection, and secure access to web applications.
Use Cases: SWGs are essential for organizations looking to protect their users from web-based threats, enforce acceptable use policies, and ensure secure access to cloud applications and web resources.